Fig. 1.
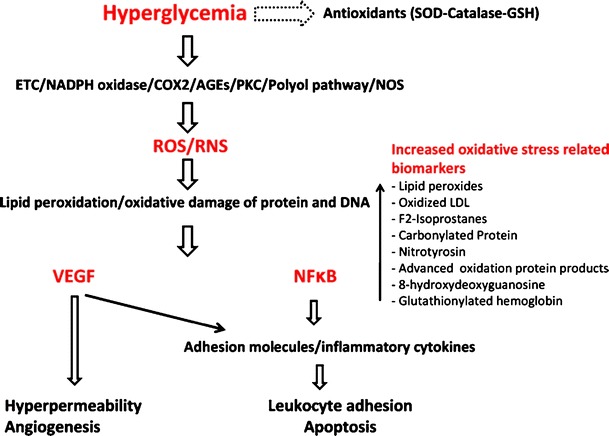
Hyperglycemia inhibits antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, glutathione (GSH)) and induces generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) from different sources such as mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC), NADPH oxidase, cycloxygenase (COX2), advanced glycation end products (AGEs), protein kinase C (PKC), polyol pathway and nitric oxide synthase (NOS). Hyperglycemia-induced generated ROS and RNS, cause lipid peroxidation and oxidative damage of protein and DNA resulting in production of biomarkers such as lipid peroxides and nitrotyrosin. Lipid and protein modification by hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress leads to upregulation of VEGF and activation of NFκB. VEGF and NFκB-dependent signaling pathway causes retinal vascular and neuronal damage associated with diabetic retinopathy such as hyperpermeability, leukostasis, apoptosis and angiogenesis
