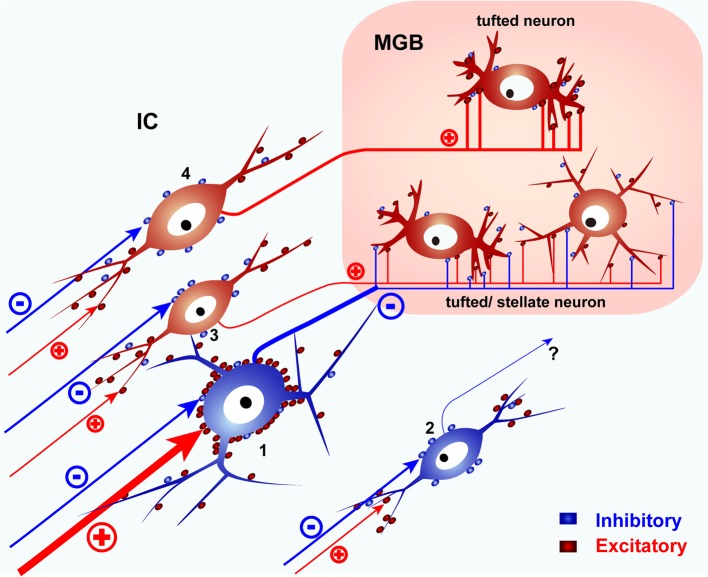
Figure 6.
A schematic diagram of the basic IC circuit. LG neurons (1) receive strong excitatory inputs on their somata, send their axons to the MGB, and presumably inhibit tufted or stellate neurons in the MGB. SG neurons (2) do not target MGB. Glutamatergic neurons (3, 4) project to the MGB but lack the dense VGLUT2 axosomatic inputs. Glutamatergic neurons with small terminals (3) co-innervate tufted or stellate neurons with LG neurons. Other tufted neurons are innervated by glutamatergic neurons with large terminals (4) and do not receive inputs from LG neurons. SG and glutamatergic neurons receive most of their excitatory inputs on their dendrites. Red puncta indicate excitatory glutamatergic terminals. Blue puncta indicate inhibitory (GABAergic and glycinergic) terminals. Modified from Ito et al. (2009).