Table 2.
Descriptive Statistics for Covariates According to Relaxation Practice (n=1036)
| Variable | Nonpractitioners (n=896)a | Practitioners (n=140)a |
|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic characteristics | ||
| Female, no. (%) | 398 (44.4) | 82 (58.6) |
| Age, mean (SD), y | 66.7 (10.1) | 63.8 (9.2) |
| Urban resident, no. (%) | 505 (56.4) | 99 (70.7) |
| Mainlander, no. (%) | 110 (12.3) | 21 (15.0) |
| Married, no. (%) | 667 (74.4) | 111 (79.3) |
| Education, mean (SD), y | 6.5 (4.8) | 8.9 (4.6) |
| Income in 2003, mean (SD), thousands NT$b | 482.2 (790.2) | 672.3 (885.3) |
| Not working/housework/ no formal job, no. (%) | 309 (34.5) | 50 (35.7) |
| Employed, no. (%) | 257 (28.7) | 45 (32.1) |
| Retired, no. (%) | 330 (36.8) | 45 (32.1) |
| Self-reported measures of health | ||
| Takes antihypertensive medication, no. (%) | 278 (31.1) | 38 (27.1) |
| Takes lipid-lowering medication, no. (%) | 63 (7.0) | 3 (2.1) |
| Takes diabetic medication, no. (%) | 138 (15.4) | 10 (7.1) |
| Any ADL limitations, no. (%)c | 74 (8.3) | 5 (3.6) |
| Mobility limitations index, mean (SD)d | 0.5 (1.3) | 0.0 (1.1) |
| CES-D, mean (SD)b,e | 5.0 (5.7) | 3.3 (4.4) |
| Ever had diabetes, no. (%) | 171 (18.0) | 14 (10.0) |
| Other current health conditions: | ||
| Heart disease, no. (%) | 150 (16.7) | 23 (16.4) |
| Lower respiratory disease, no. (%) | 61 (6.8) | 5 (3.6) |
| Arthritis, no. (%) | 137 (15.3) | 21 (15.0) |
| Gastric ulcer or stomach ailment, no. (%) | 130 (14.5) | 14 (10.0) |
| Liver or gallbladder disease, no. (%) | 69 (7.7) | 14 (10.0) |
| Cataracts, no. (%) | 160 (17.9) | 25 (17.9) |
| Kidney disease, no. (%) | 49 (5.5) | 6 (4.3) |
| Gout, no. (%) | 76 (8.5) | 9 (6.4) |
| Spinal/vertebral spur, no. (%) | 88 (9.8) | 14 (10.0) |
| Interviewer-administered health assessments | ||
| Cognitive function, mean (SD) b,f | 16.4 (3.6) | 17.9 (2.3) |
| Unable to perform grip strength test, no. (%)g | 29 (5.2) | 2 (2.9) |
| Grip strength, mean (SD), kgh | 27.7 (10.6) | 27.8 (10.2) |
| Unable to perform peak flow test, no. (%)b,g | 25 (2.8) | 2 (1.4) |
| Peak flow, mean (SD), L/minh | 331.8 (140.2) | 361.2 (132.6) |
| Unable to perform timed walk, no. (%)g,i | 33 (3.7) | 1 (0.7) |
| Normal walking speed, mean (SD), m/sec h,i | 0.84 (0.29) | 0.95 (0.26) |
| Unable to complete chair-stand test, no. (%)g,j | 80 (9.0) | 4 (2.9) |
| Chair-stand speed, mean (SD), stands/sech,j | 0.51 (0.19) | 0.56 (0.18) |
| Exercise | ||
| None, no. (%) | 436 (48.7) | 53 (37.9) |
| Low/moderate, no. (%) | 194 (21.7) | 23 (16.4) |
| Regular, no. (%) | 265 (29.6) | 64 (45.7) |
Unless otherwise specified, missing comprise fewer than 1% of the sample. Statistics are based on cases with valid data.
Missing for 1%-4% of the sample.
Includes respondents who report having any difficulty performing six ADLs without assistance: bathing; dressing/undressing; eating; getting out of bed/standing up/sitting in a chair; moving around the house; and using the toilet.
Based on self-reported difficulty performing 8 physical tasks without assistance: standing for 15 minutes, squatting, reaching over one's head, grasping with fingers, lifting/carrying 11–12 kg, running 20-30 m, walking 200–300 m, and climbing two or three flights of stairs. Each item is coded as follows: 0=no difficulty, 1=some difficulty, 2=great difficulty, 3=unable. On the basis of the validation and recommendations of Long and Pavalko,25 the index was constructed by summing the 8 items, adding a constant (0.5), and taking the logarithm of the result (observed range: −0.7 to 3.2).
Depressive symptoms are measured by a 10-item short form of the full CES-D, coded according to standard practice based on both the number and severity of symptoms (potential range: 0–30; observed range: 0–27).
Score is based on the number of cognitive tasks completed correctly, including basic orientation questions, a series of four subtractions, and immediate memory recall (potential range: 0–24; observed range: 0–23).
The respondent was coded as unable to perform the test if: s/he met the exclusion criteria;19 s/he attempted but was unable to perform the test or stopped because of discomfort, weakness, or frailty; or the respondent/interviewer felt it would be unsafe. The test was coded as missing if the respondent refused, was unable to understand or cooperate with the instructions, the equipment failed, or in the case of the chair-stand test, no suitable chair was available.
Among those able to perform the test.
Respondents were asked to walk 3 m (n=9 walked 2–2.5 m because of space limitations) at their normal speed, using a walking aid if needed. Walking speed was calculated as the recorded distance divided by the completion time for the faster of two trials.
The respondent was asked to stand up and sit down again 5 times in a row as quickly as possible without stopping; an armless, straight-back chair with a hard seat was used. For those able to complete five stands, the completion time was recorded. To adjust for differences in chair height, we regressed the completion time (ci) for individual i on chair height (hi) controlling for the respondent's age and height, separately for men and women.26 The adjusted chair stand completion time is calculated as 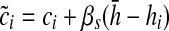 , where βs is the coefficient for chair height (hi) from the sex specific model and
, where βs is the coefficient for chair height (hi) from the sex specific model and 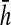 is the mean chair height among the entire sample. Chair-stand speed is computed as 5 divided by the adjusted time
is the mean chair height among the entire sample. Chair-stand speed is computed as 5 divided by the adjusted time 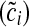 .
.
ADL, Activities of Daily Living; CES-D, Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression scale; NT$, New Taiwan dollar; SD, standard deviation.
