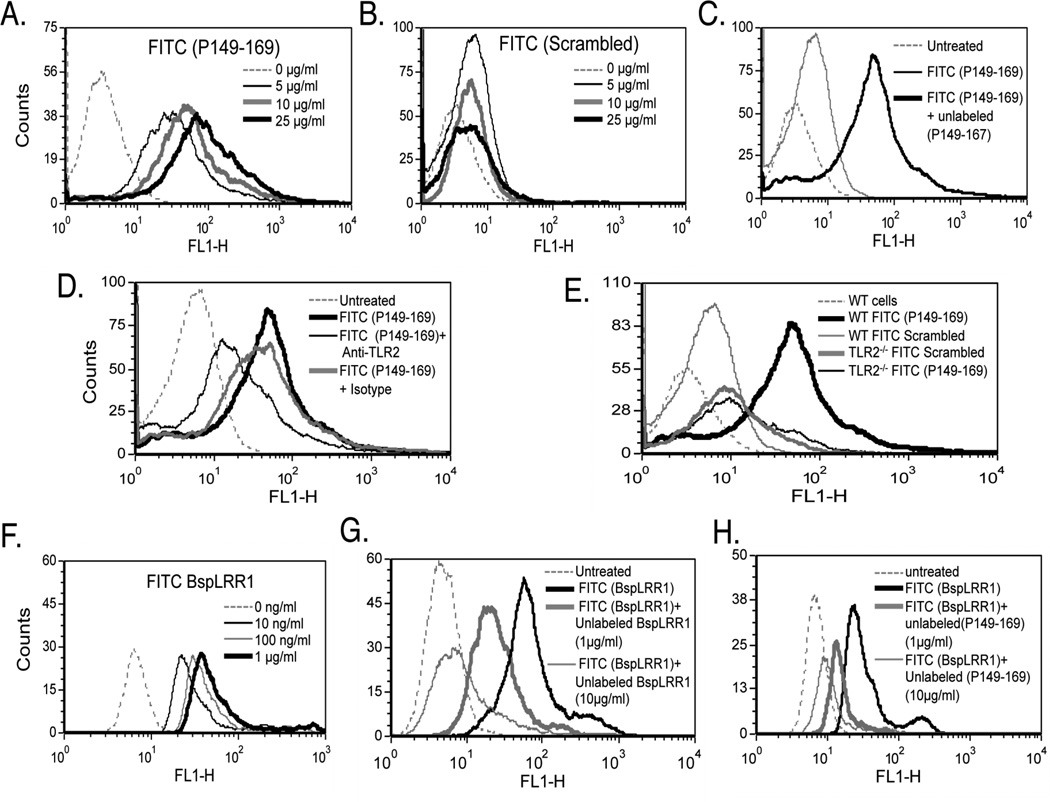
Fig. 4.
TLR2-activating epitope of BspA specifically binds TLR2. (A & B) HEK293 (hTLR2/hTLR1) cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of the fluorescently labeled peptide P149–169 (A) or the scrambled peptide (B) and analyzed by flow cytometry. (C & D) Flow cytometry of HEK293 (hTLR2/hTLR1) cells preincubated with the unlabeled peptide P149–169 (25 µg/ml; 5 min) (C) or preincubated with anti-TLR2 or isotype control (IgG2a) antibody (each at 5 µg/ml; 15 min) (D) followed by incubation with labeled P149–169 peptide (5 µg/ml; 15 min). (E) WT and TLR2−/− mouse macrophages were incubated with fluorescently labeled peptides (P149–169 or scrambled). (F) HEK293 (hTLR2/hTLR1) cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of the fluorescently labeled peptide rBspLRR1. (G & H) Cells were preincubated with either the unlabeled rBspLRR1 (1 & 10 µg/ml; 5 min) (G) or unlabeled peptide P149–169 (1 & 10 µg/ml; 5 min) (H) prior to incubation with labeled rBspLRR1-(100 ng/ml; 15 min). Data in each panel are representative of three to four independent experiments.