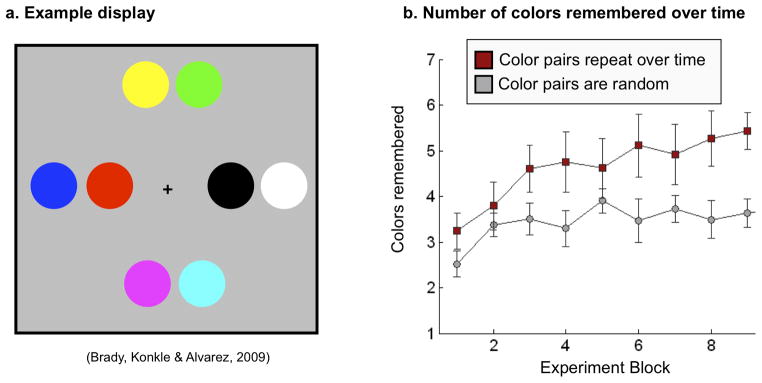
Figure 4.
Effects of learned knowledge on visual working memory. (a) Example memory display modeled after Brady, Konkle, & Alvarez (2009). The task was to remember all 8 colors. Memory was probed with a cued-recall test: a single location was cued, and the observer indicated which color appeared at the cued location. (b) Number of colors remembered over time in Brady, Konkle & Alvarez (2009). One group of observers saw certain color pairs more often than others (e.g., yellow and green might occur next to each other 80% of the time), whereas the other group saw completely random color pairs. For the group that saw repeated color pairs, the number of color remembered increased across blocks, nearly doubling the number remembered by the random group by the end of the session.