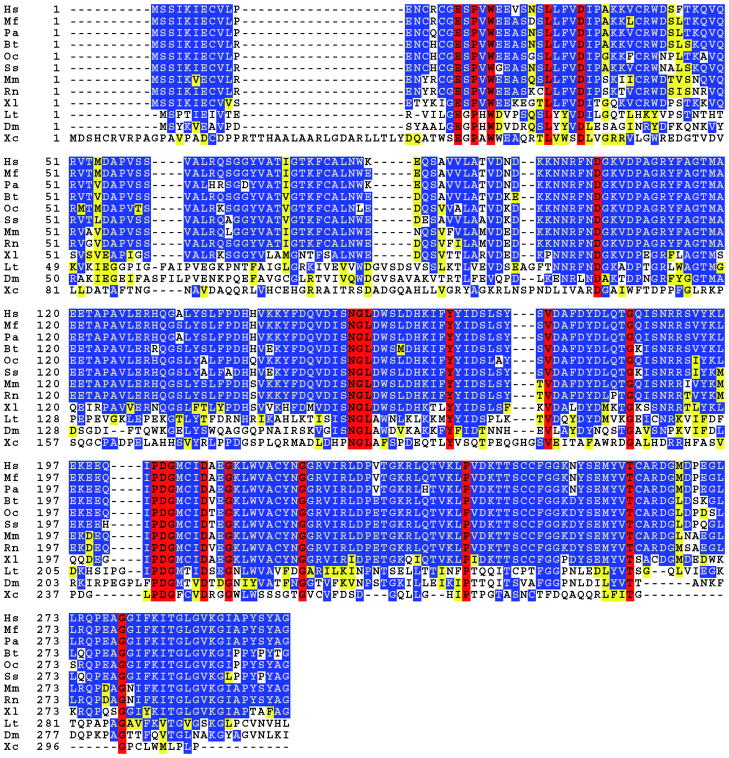
Figure 1.
Amino acid sequence alignment of SMP30 homologs in vertebrates and invertebrates. Red indicates completely conserved, blue indicates identical, and yellow indicates similar residues. Identity between vertebrates ranges from 70–90%, and drops to about 30% between vertebrate and invertebrate forms of SMP30. The amino acid sequence of SMP30 is highly conserved among all mammals, regardless of ability to synthesize ascorbate. Latin and common names as well as gi accession numbers for the above represented species are as follows: Hs, Homo Sapiens, human, 23111021; Mf, Macaca fascicularis, monkey, 115502619; Pa, Pongo abeilii, orangutan, 197101437; Bt, Bos Taurus, cow, 13633941; Oc, Oryctolagus cuniculus, rabbit, 20178120; Ss, Sus scrofa, pig, 122131846; Mm, Mus musculus, mouse, 15215231; Rn, Rattus Norvegicus, rat, 68067383; Xl, Xenopus laevis, frog, 147905135; Lt, Lampyris turkestanicus, firefly LRE, 301068495; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster, fruit fly, 23171287; Xc, Xanthomonas campestris, bacteria, 21233020. This sequence alignment was prepared using the Biology Workbench (81).