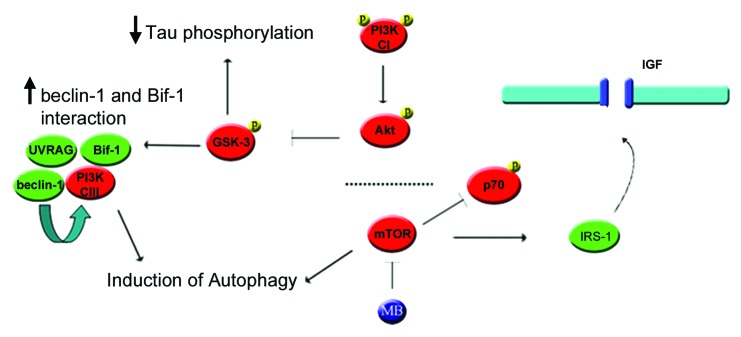
Figure 10. Proposed mechanism by which MB could stimulate autophagy through mTOR and Akt. (1) Inhibition of mTOR induces autophagy directly but also reduces phosphorylation of IRS1. (2) Dephosphorylation of IRS-1 results in decreased degradation and increased binding to the IGF receptor, increasing the receptor’s basal activity level. (3) Higher basal IGF receptor activity leads to increased phosphorylation of the PIK3R3/p55 and PIK3R1/p85 regulatory subunits of PtdIns 3-kinase (CI), thus increasing its activity. (4) PI3 kinase (CI) phosphorylates Akt. This in turn phosphorylates GSK-3 at the inhibitory site, lowering its activity. (5) In addition, reduced GSK-3 activity can lead to increased Bif-1 interaction with BECN1. (6) The SH3GLB1-BECN1 complex activates PtdIns 3-kinase (CIII) through UVRAG, stimulating autophagy.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.