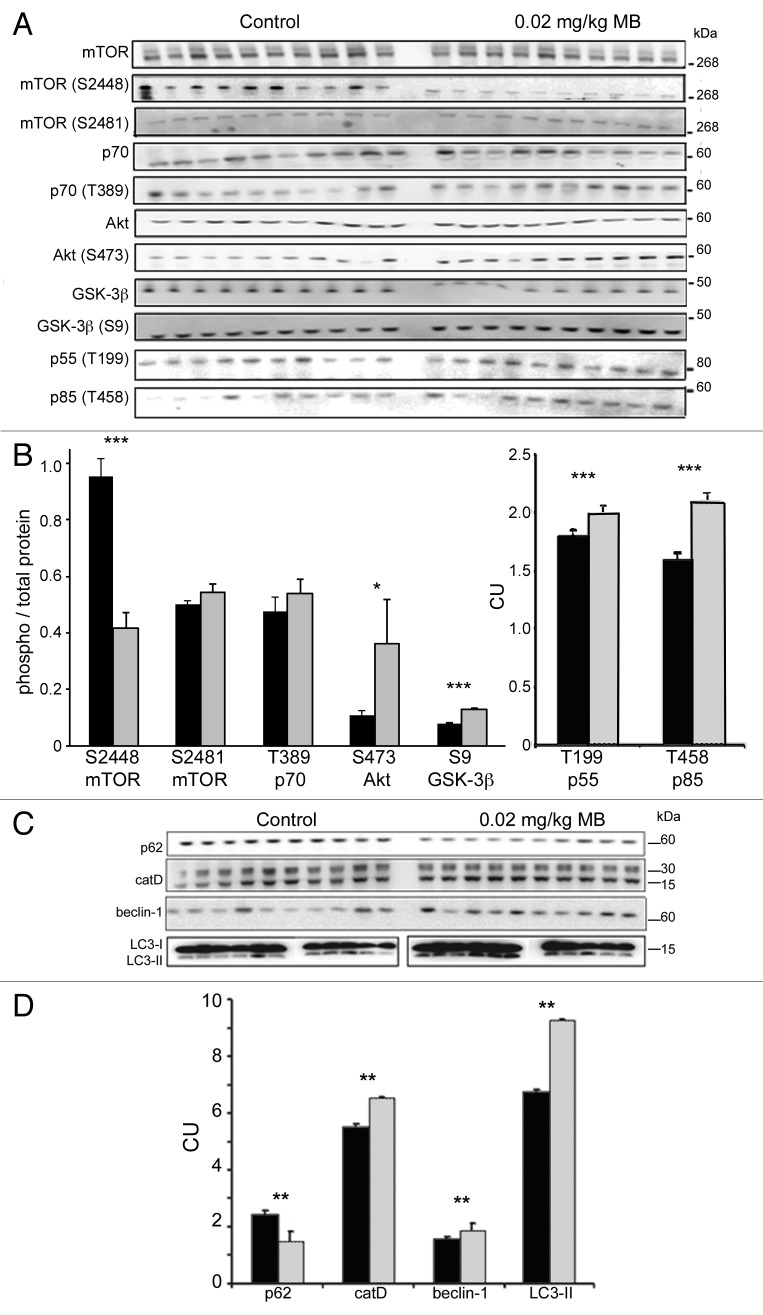
Figure 9.
MB alters kinase activity and biomarkers of autophagy and lysosomes. Similar to the cell study shown in Figure 7, levels of total and phosphorylated epitopes of mTOR, p70S6K, Akt and GSK-3β were determined by immunoblotting (A). The ratio between the corresponding phosphorylated epitope and total kinase was determined, for vehicle (black bars) and MB treated (gray bars) animals (B). MB treatment results in a significant reduction of the phospho-mTOR ser2448 to mTOR ratio. The ratio of phospho-mTOR ser2481 and phospho-p70 thr389 (to total protein) unchanged. The ratio of phospho-Akt ser473 and phospho-GSK-3β ser9 (to total protein) was significantly increased with MB treatment. Levels of p55 thr199 and p85 thr458, regulatory subunits of PI3 kinase C1 were also significantly increased relative to control levels. (C) shows immunoblots prepared from JNPL3 mice probed for autophagy markers p62, cathepsin D, BECN1 and LC3. (D) shows quantification of the immunoblots. Treatment with 0.02 mg/kg MB (gray bars) led to a significant change in several markers of autophagy relative to vehicle-treated animals (black bars) including p62, BECN1 and cathepsin D. LC3-II levels were significantly increased in MB treated animals relative to vehicle. For all, control and MB treated samples were run on the same blot. LC3-II samples were run on smaller gels but loading order is the same. Significance levels indicated by *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.