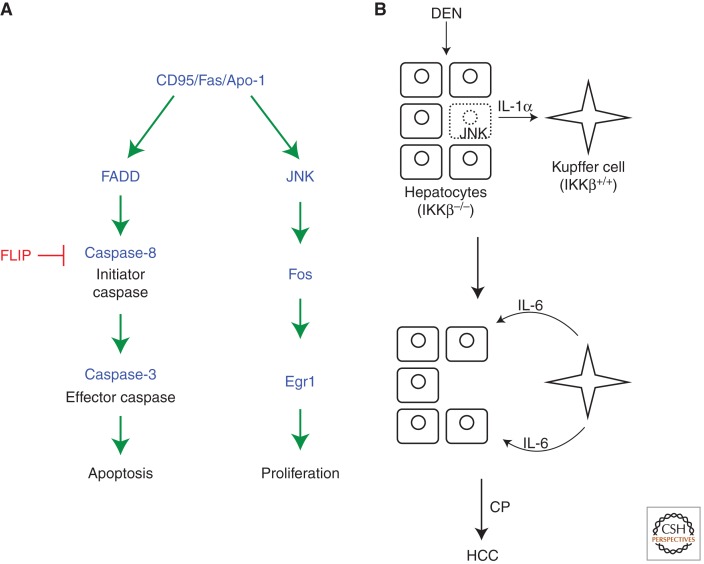
Figure 5.
Potential models of apoptosis-induced proliferation in mammals. (A) The CD95/Fas/Apo1 pathway in apoptosis and proliferation. The CD95/Fas/Apo1 receptor induces apoptosis through the very well-studied FADD/Caspase-8 pathway. FLIP is a Caspase-8 analog and acts as a dominant negative for Caspase-8 activation. The proliferation component of CD95/Fas/Apo1 is less characterized, but appears to engage the JNK pathway. (B) Role of compensatory proliferation for development of hepatocarcinoma (HCC). Loss of IKKβ or IKKγ renders hepatocytes extremely sensitive to carcinogens such as diethylnitrosoamine (DEN), causing JNK-induced cell death (stippled cell). However, JNK also induces expression of interleukin-1α (IL-1α). IL-1α induces the production of IL-6 in Kupffer cells. IL-6 feeds back onto surviving hepatocytes and induces proliferation and subsequently HCC. Interestingly, because IL-1α induces NF-κB activation, Kupffer cells need to be wild-type for IKKβ and IKKγ for apoptosis-induced proliferation and HCC to occur. (Panel based on data modified from He and Karin [2011].)