Figure 4.
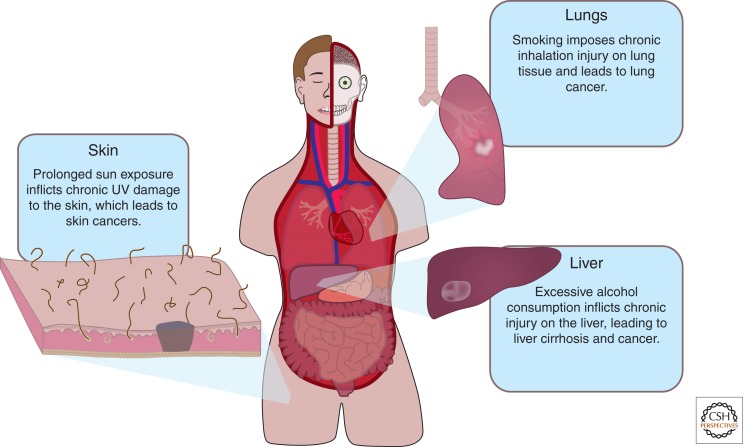
Does chronic injury lead to prolonged Wnt signaling and cancer? Injury results in a local increase in Wnt signaling and chronic injury leads to cancer. Many cancers also have up-regulated Wnt signaling. The Wnt pathway is best known to promote proliferation; an intriguing possibility is that chronic injury may induce a prolonged Wnt response leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation and cancer. In the lungs, cigarette smokers inflict chronic injury to the trachea and lung tissue, which may result in lung cancer. Relating to the skin, prolonged UV exposure leads to chronic inflammation of the dermis, which may result in skin cancer. In the liver, chronic alcohol consumption subjects the tissue to constant damage, which may lead to liver cancer.