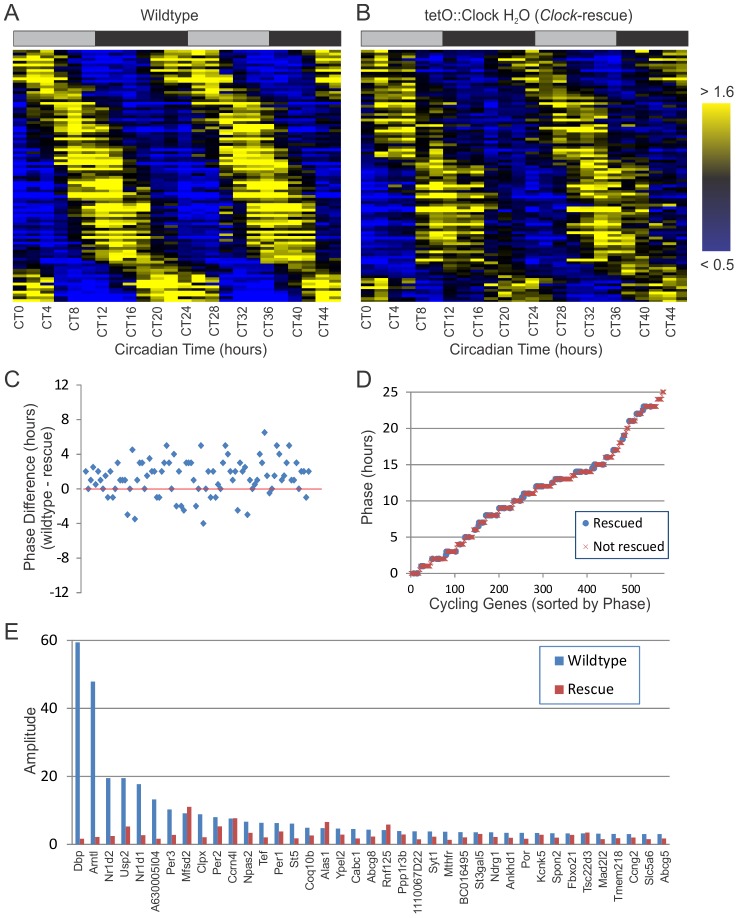
Figure 4. Clock-rescue restores appropriate phase to circadian output genes.
24-hour cycling genes (p<0.0011 for both genotypes, period ≥20 hours, N = 92) identified in both wildtype (A) and Clock-rescue animals (B) were median-normalized, sorted by phase, and plotted as a heatmap (yellow = high expression, blue = low expression). Each row represents the temporal expression of one cycling gene common to both datasets. Shaded bars above the heatmaps represent subjective day and night. In (C), the phase difference between wildtype and Clock-rescue is plotted for all 92 rescued genes, ordered by amplitude in wildtype. On average, there is a ∼1.5 h phase advance in the Clock-rescue samples. Panel (D) shows the phases of every cycling gene identified in wildtype, including those rescued in Clock-rescue animals (blue circles) and those not rescued (red x's). There was no bias in the phase of rescued genes. Panel (E) shows the amplitudes of high-amplitude cycling genes (AMP>3.0) in wildtype versus Clock-rescue animals. Several genes have been re-plotted from Figure 2E for the sake of completeness.