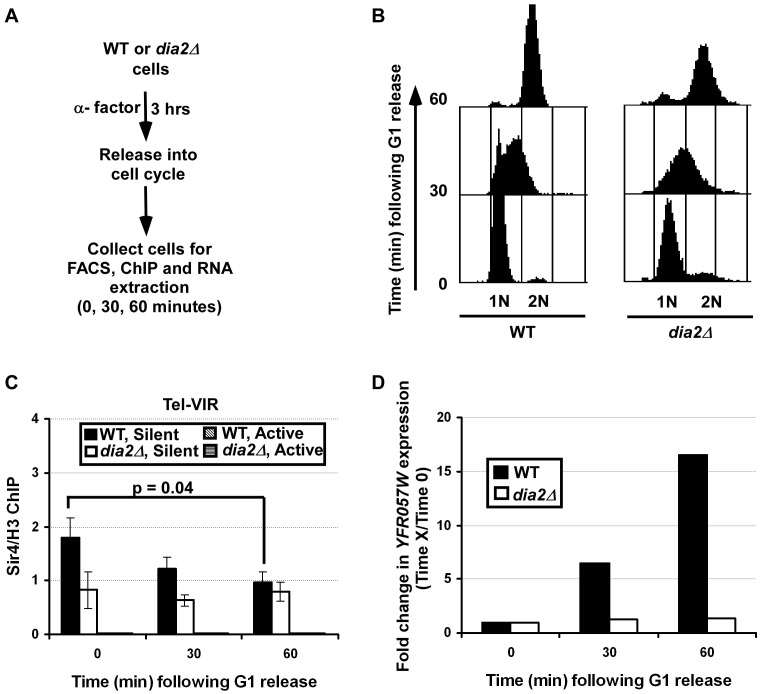
Figure 7. Sir4 binding at telomeric silent chromatin and expression of a telomeric gene are regulated during the cell cycle in a Dia2-dependent manner.
(A) Schematic representation of the experiments to test Sir4 binding and gene expression at telomeric silent chromatin during the cell cycle. Briefly, WT or dia2Δ cells were arrested at G1 with α-factor. Samples were collected for analysis of DNA content (B), Sir4 ChIP (C) and (D) gene expression at 0, 30 and 60 minutes following released into cell cycle. (B) Cell cycle analysis of WT and dia2Δ cells collected in the experiment described in A. DNA was stained using propidium iodide and analyzed using flow cytometry. (C) Sir4 binding is reduced at telomere silent chromatin as cells progress through the cell cycle, whereas Sir4 levels in dia2Δ mutant cells are not changed during the cell cycle. At each time point, cells were collected for ChIP assay using antibodies against Sir4 and histone H3. ChIP DNA was analyzed by real time PCR using PCR primers amplifying both silent and active chromatin loci as described in Figure 5D. The Sir4 ChIP signal was normalized against that of H3. The data presented is the average ± s.d. of three independent experiments with the p-value indicated as determined using the student's t-test. (D) The expression of the YFR057W increases as the cell cycle progresses. RNA was isolated from cells collected at each time point and reverse transcribed. The expression of YFR057W was analyzed using quantitative real-time PCR and was normalized against the expression of ACT1 as described in Figure 1E. Data is presented as the ratio of the relative expression of YFR057W at each indicated time point to the YFR057W expression at the G1 phase (0) time point for the respective cell type (thus, YFR057W expression at time 0 is 1 for both genotypes). The average calculated from two independent experiments is shown.