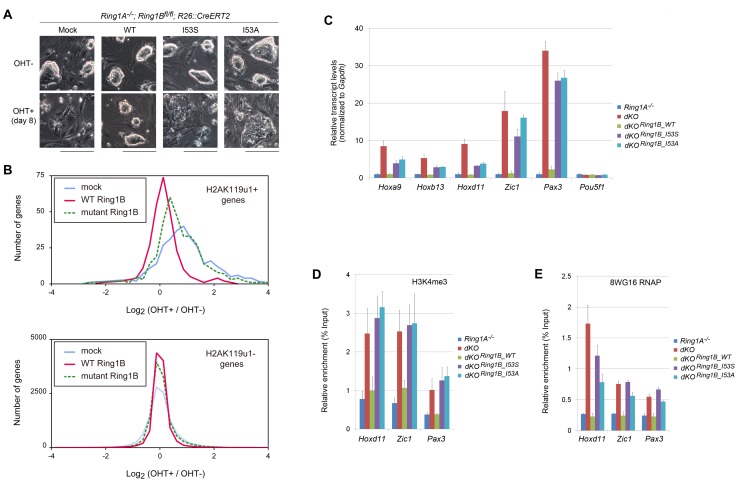
Figure 3. H2A ubiquitination activity of Ring1B is essential for the maintenance of ESC identity and repression of target gene expression.
(A) Morphology of OHT-untreated and –treated (day 8) Ring1A−/−; Ring1Bfl/fl; R26::CreERT2 ESC lines expressing the indicated transgene. The images were acquired under a phase-contrast microscope. Scale bars indicate 200 µm. (B) Histograms showing the expression changes of H2AK119u1+ and H2AK119u1− genes in Ring1A−/−; Ring1Bfl/fl; Rosa26::CreERT2 ESCs expressing mock (blue line), WT Ring1B (red line), or mutant Ring1B (green dotted line) following OHT treatment. (C) Expression levels of Hoxa9, Hoxb13, Hoxd11, Zic1, Pax3 and Pou5f1 in Ring1A−/−; Ring1Bfl/fl; Rosa26::CreERT2 ESCs expressing mock, WT, I53S, or I53A Ring1B before (−) or after (+) OHT treatment (day 2). Expression levels were normalized to a Gapdh control and are depicted as fold changes relative to mock (OHT-untreated) ESCs. Error bars represent standard deviation determined from at least three independent experiments. (D) Local levels of trimethylated H3K4 (H3K4me3) at promoter regions of representative target genes in Ring1A−/−; Ring1Bfl/fl; R26::CreERT2 ESCs stably expressing mock, WT, I53S, or I53A Ring1B before (−) or after (+) OHT treatment (day 2) were determined by ChIP and site-specific real-time PCR. The relative amount of immunoprecipitated DNA is depicted as a percentage of input DNA. Error bars represent standard deviation determined from at least three independent experiments. (E) As in (D), but showing local levels of RNA polymerase II (RNAP) detected with the 8WG16 antibody.