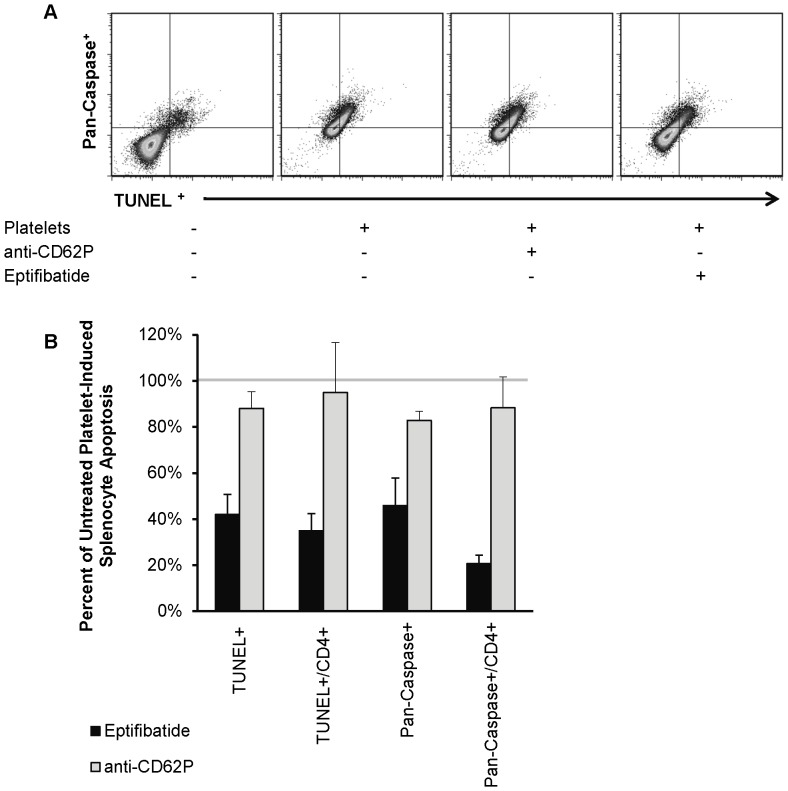
Figure 4. Eptifibatide reduces septic platelet-induced splenocyte apoptosis ex vivo.
A. Representative flow cytometry staining of CD4+ splenocytes for pan-caspase FLICA (Y axis) vs. TUNEL (X axis) in presence of (left-to-right) no platelets, septic platelets, septic platelets with anti-62P antibody, or septic platelets with eptifibatide. B. Shown is the mean±SEM percent of septic platelet-induced splenocyte and CD4+ splenocyte apoptosis (i.e. TUNEL+ and pan-Caspase+) compared between pretreatment conditions (i.e. eptifibatide and anti-CD62P). These results were normalized to the level of apoptosis in splenocytes incubated with untreated septic platelets (solid line). Both splenocytes overall and CD4+ splenocytes showed a significant reduction (p<0.05) in apoptosis when platelets were pre-treated with eptifibatide. Pretreatment with an anti-CD62P monoclonal antibody did not significantly alter platelet-induced splenocyte apoptosis.