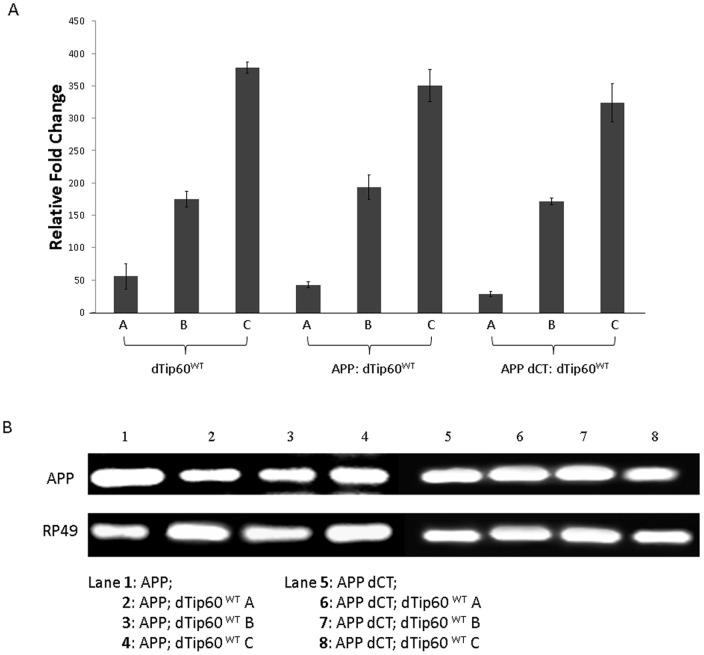
Figure 2. Generation and characterization of dTip60WT containing APP or APP-dCT double transgenic flies.
Flies expressing varying levels of wild type dTip60 (low, medium and high) were generated and then each introduced into APP or APP dCT background using standard genetic techniques. (A) The amount of wild type dTip60 that is exogenously induced relative to endogenous dTip60 was quantified by RT-PCR analysis of staged F1 second instar larvae resulting from the a cross between the ubiquitous driver 337 and either dTip60WT (lines A, B and C), APP; dTip60WT (lines A, B and C) or APP dCT; dTip60WT (lines A, B and C). 337-Gal4 crossed to w1118 was used as control. The relative fold change in mRNA expression levels between exogenous and endogenous dTip60 was measured as described before using the comparative CT method with RP49 as the internal control, and these results are summarized in the histogram. The amount of exogenously induced wild type dTip60 levels is significantly different between lines A, B and C in each case with values of p<0.05; n = 3. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. (B) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of APP or APP dCT expression in the different dTip60WT containing transgenic lines to confirm APP transgene presence. cDNA was prepared as before from staged second instar larvae ubiquitously expressing dTip60WT with APP or APP dCT (lines A, B or C in each case) and PCR amplified using primers that flank a 100 bp region in the N-terminal portion of APP. PCR products were visualized using 2% agarose gel containing ethidium bromide. Staged second instar larvae ubiquitously expressing APP or APP dCT were used as controls.