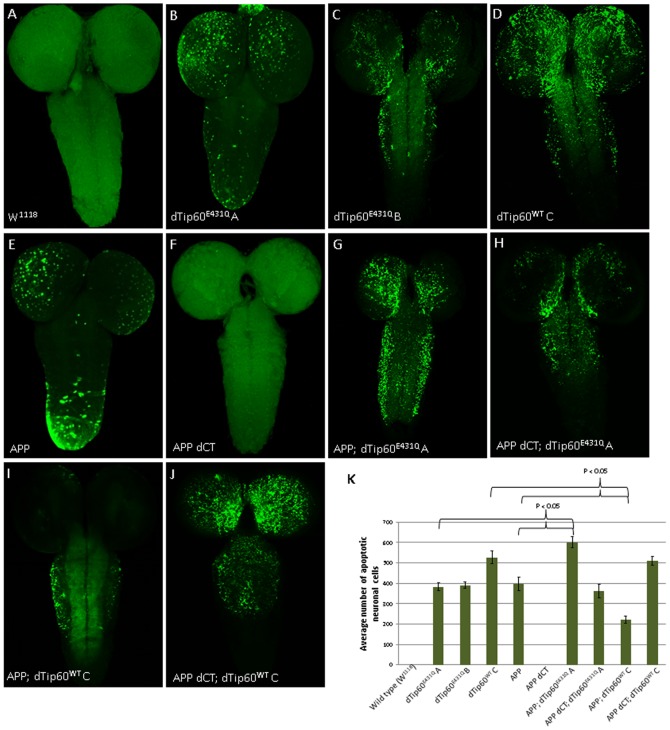
Figure 5. dTip60 mediates APP induced apoptotic neuronal cell death in the Drosophila central nervous system.
Representative confocal images of neuronal apoptosis visualized by TUNEL staining of brains from staged third instar larvae expressing indicated transgenes driven by pan-neuronal driver 179-GAL4. The w1118 larvae used as genetic background control showed no apoptosis (A). Pan neuronal expression of dTip60E431Q induces apoptosis in a dose independent manner as evident from comparable levels of apoptosis seen in fly lines expressing low (B) or high (C) levels of dTip60E431Q. Overexpression of wild type dTip60 increased neuronal cell death due to apoptosis (D). The C-terminal domain of APP induces apoptosis as evident from TUNEL positive apoptotic cells in flies overexpressing APP (E) while no apoptosis was observed in flies expressing a truncated version of APP lacking the C-terminal domain (F). Co-expression of APP with low levels of dTip60E431Q (dTip60E431Q A) enhances the severity of apoptosis phenotype in a synergistic manner (G) that is dependent on the APP C-terminal domain. Co-expression of APP lacking C-terminus with dTip60E431Q A exhibited apoptosis that was comparable to that seen when dTip60E431Q A was expressed alone (H). Overexpression of wild type dTip60 in the APP overexpressing background partially rescued the apoptosis phenotype (I) but in the presence of APP lacking C-terminus exerted similar severity seen in flies overexpressing wild type dTip60 alone. Images shown represent projections of 1 um confocal slices. Apoptotic cells in the different genotypes were quantified by counting the number of TUNEL positive cells in the entire fly brain (K).