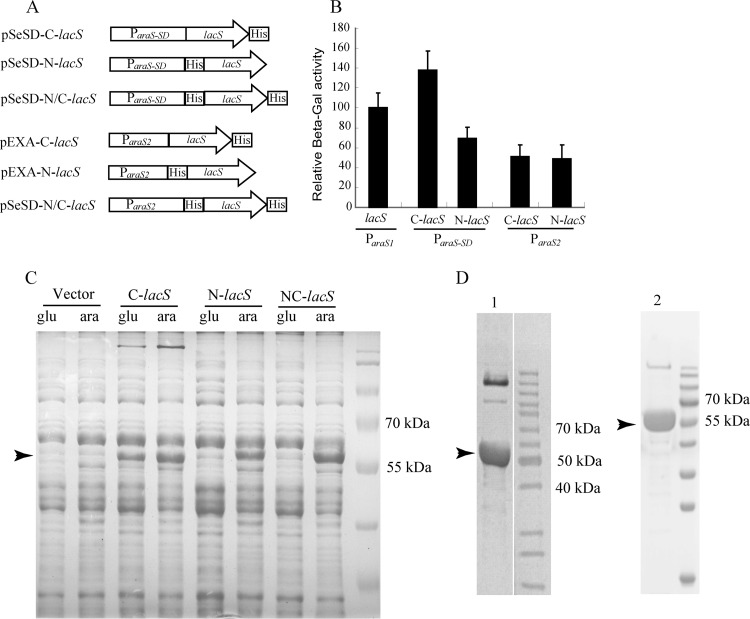
Fig 3.
Characterization of recombinant β-galactosidase proteins carrying different 6×His tags expressed from ParaS-SD and ParaS2. (A) Schematic diagrams of six plasmids expressing 6×His β-glycosidase fusion proteins from ParaS-SD (pSeSD) or ParaS2 (pEXA). The features of the two vectors and the promoters present in their expression cassettes are shown in Fig. 1. (B) Relative activity of the recombinant β-glycosidase proteins expressed from the two promoters. Strains carrying each plasmid were grown in ACVy to an OD600 of ca. 0.2. Cell mass from which cell extracts were prepared was collected for each culture and used for determining β-galactosidase (β-Gal) activity. The activity of the reporter plasmid pRp (21) was set to 100% and used as a reference to normalize the specific activity of recombinant β-glycosidase enzymes expressed from other plasmids. Assays were conducted in triplicate. (C) SDS-PAGE of recombinant β-glycosidase proteins produced from pSeSD constructs. Strains carrying each plasmid were grown in either GCVy (glu) or ACVy (ara) to an OD600 of ca. 0.2. Cell mass from which cell extracts were prepared was collected for each culture. Equal amounts of cell lysates were loaded onto a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel to visualize the recombinant proteins in the context of total protein. The arrowhead indicates the position of the recombinant proteins. (D) Recombinant proteins purified from the overexpression strains carrying pEXA-C-lacS (lane 1) and pEXA-N/C-lacS (lane 2). Cultures were grown in ACVy as described above, and 6×His-tagged recombinant proteins were purified using a nickel-affinity column. Recombinant protein produced from pEXA-N-lacS could not be purified by His tag-affinity chromatography. Arrowheads indicate the protein bands that were transferred onto a membrane and sent for determination of their N-terminal amino acid sequences. The sequencing results are presented in Table 2.