Fig. 3.
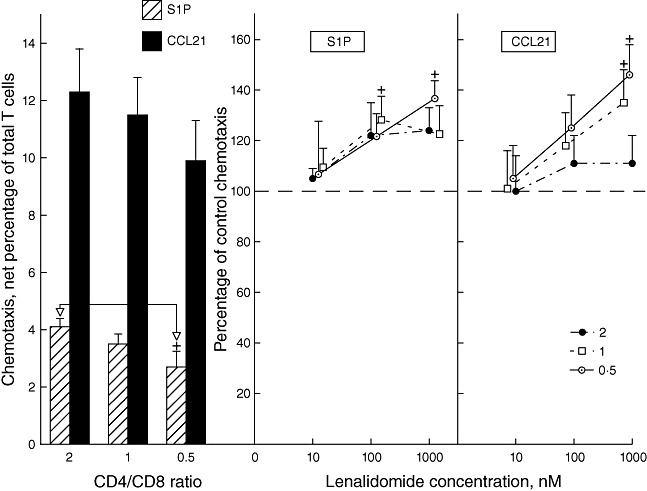
Influence of CD4 : CD8 T cell ratio on healthy male human T cell chemotaxis and the effects of lenalidomide on T cell chemotaxis. Left-hand frame: each column and bar depicts the mean ± standard deviation (s.d.) of the chemotactic responses of T cells from three human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-negative healthy male subjects to 10−7 M sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) and 3 × 10−8 M chemokine CCL21, as a percentage of the 106 T cells introduced initially into the upper chamber. The statistical significance of one difference in chemotaxis to S1P between T cells at a CD4/CD8 ratio of 0·5 compared to those at a ratio of 2 is shown by+P < 0·05. Right-hand frames: each point and bar depicts the mean ± s.d. of the chemotactic responses of lenalidomide-treated T cells from the three subjects to 10−7 M S1P and 3 × 10−8 M CCL21, as a percentage of the chemotaxis of the same T cells without lenalidomide treatment (100%). Statistical significance of differences between chemotaxis of lenalidomide-treated and control T cells is shown as in Fig. 1.
