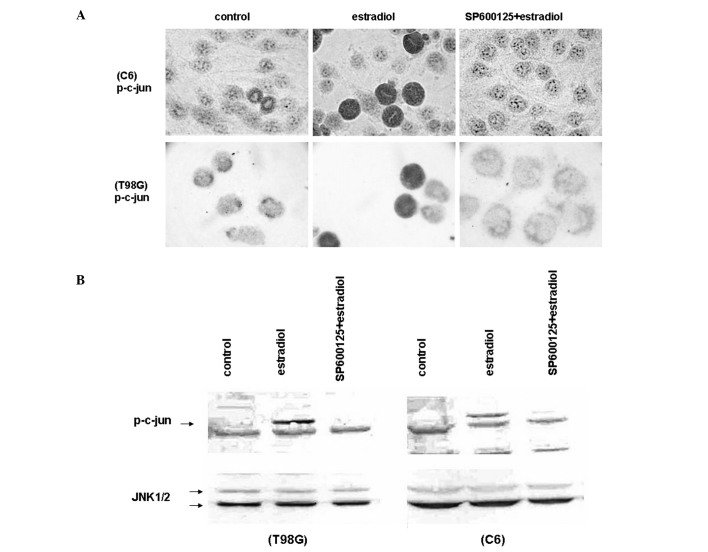
Figure 3.
Estradiol induced JNK activation. (A) Immunocytochemical analysis showing c-jun phosphorylation (p-c-Jun) in C6 cells (upper panel) and in T98G cells (lower panel) pretreated with 20 μM SP600125 or vehicle (control) for 30 min, and incubated with 20 μM estradiol for 18 h under low growth-stimulated conditions. Phosphorylation of c-jun was visualized by anti-phosphorylated-c-jun antibody. Cells were visualized by using biotinylated secondary antibody, streptavidin/HRP and AEC chromogen. Images were captured using a brightfield microscope at a magnification of ×600. (B) Western blot analysis for the level of phosphorylated c-Jun (p-c-Jun) in C6 cells (right panel) and in T98G cells (left panel) pretreated with 20 μM SP600125 or vehicle (control) for 30 min, and incubated with 20 μM estradiol, for 18 h under low growth-stimulated conditions. Cell lysates were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and Western blotted with polyclonal antibody against the phosphorylated form of c-jun (upper panels). The corresponding native proteins of JNKs from the same lysates were blotted in separate membranes and shown in the lower panels. The blots were then visualized by using alkaline phosphatase conjugated secondary antibodies and BCIP/NBT as substrates.