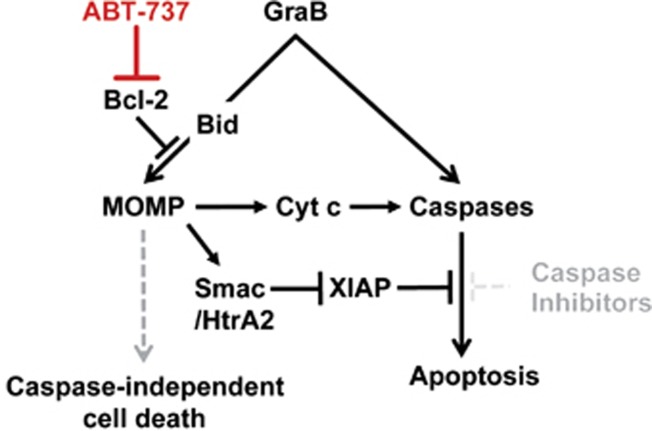
Figure 6.
Restoration of cell death by ABT-737 in cancer cells that overexpress Bcl-2 and caspase activity is blocked. GraB can activate a mitochondria-dependent pathway to cell death by cleaving Bid (left), which triggers MOMP. This pathway can be blocked by overexpression of Bcl-2. GraB can also trigger apoptosis by cleaving caspases directly (right) and this pathway can be blocked by overexpression of caspase inhibitors, such as XIAP. Cell death can therefore be achieved by the complementary pathway if only one pathway is blocked. In cases where both pathways are blocked, neutralising Bcl-2 with ABT-737 is sufficient to restore the mitochondrial pathway. This results in apoptosis by activation of caspases, which can be achieved directly via cyt c or indirectly by Smac/HtrA2 that can neutralise some caspase inhibitors. MOMP can also cause caspase-independent cell death as a consequence of mitochondrial damage. Restoration of GraB-induced MOMP by neutralising Bcl-2 will therefore cause death of the cell even if caspase activity cannot be restored