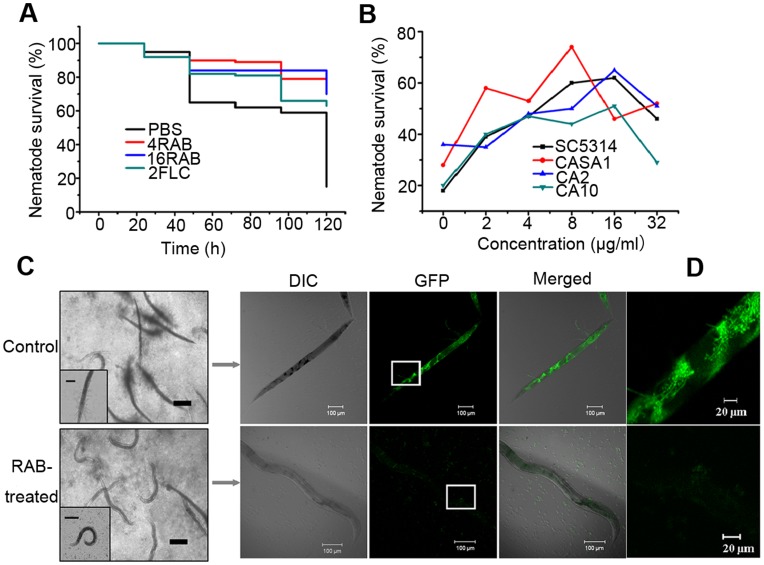
Figure 2. RAB confers improved nematodes’ survival by retarding the formation of invasive hyphae.
(A) Nematodes were infected with C. albicans YEM30 for 2 h and then moved to pathogen-free liquid media in the presence of PBS (negative control), RAB (4 or 16 µg/ml) or 2 µg/ml of FLC (positive control). Each day the worms were monitored and the survival rate was calculated. p<0.001 for 4RAB, 16RAB and FLC treated groups compared to PBS-treated group. (B) Nematodes were infected with the indicated C. albicans strains and then treated by a series of doses of RAB. After 5 days of therapy, the survival ratio in each group was calculated. (C) The nematodes were infected by C. albicans strain CASA1 with GFP tagged CDR1 for 2 h and then moved into pathogen-free liquid media containing drugs or the vehicle for 5 days. And then they were observed in 4× objective magnification. Most nematodes in control group did not demonstrate any movement and developed filaments outside the body. However, the majority of the drug-treated were alive and not invaded by the hyphae (scale bars: 200 µm). Insert shows the images of nematodes captured at 200× magnification (scale bars: 100 µm). The representative worm was selected for confocal microscopic observation. Green fluorescence of hyphae cells and yeast cells was seen within the intestine of the dead nematode under the vehicle treatment. And no C. albicans cells were observed in the live worm challenged by RAB (about 60 nematodes in each group). (D) Enlarged view of the rectangle frame.