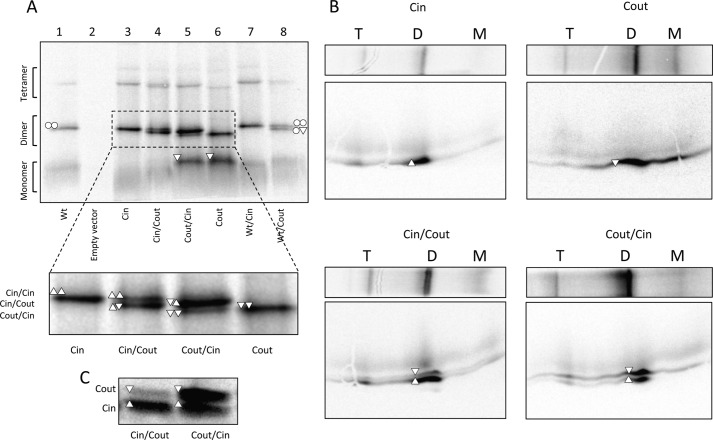
FIGURE 2.
Analysis of dimer formation by BN-PAGE. A, BN-PAGE of EmrE(WT) (○), EmrE(Cin) (△), EmrE(Cout) (▿), and co-expressed versions. Monomeric (M), dimeric (D), and tetrameric (T) forms and their composition are indicated. Note that EmrE(Cout) migrates faster than EmrE(Cin) and EmrE(WT) on BN-PAGE, opposite to the situation for SDS-PAGE. B, two-dimensional SDS-gel of BN-PAGE separated samples of EmrE(Cin), EmrE(Cout), co-expressed EmrE(Cin)/EmrE(Cout), and co-expressed EmrE(Cout)/EmrE(Cin). C, SDS-PAGE of the same samples as in A and B (co-expressed EmrE(Cin)/EmrE(Cout) and co-expressed EmrE(Cout)/EmrE(Cin)), illustrating that the relative expression levels depend on the cloning site (MCS1, MCS2) in the vector. The protein encoded by the gene in MCS1 tends to be more highly expressed than the gene in MCS2.