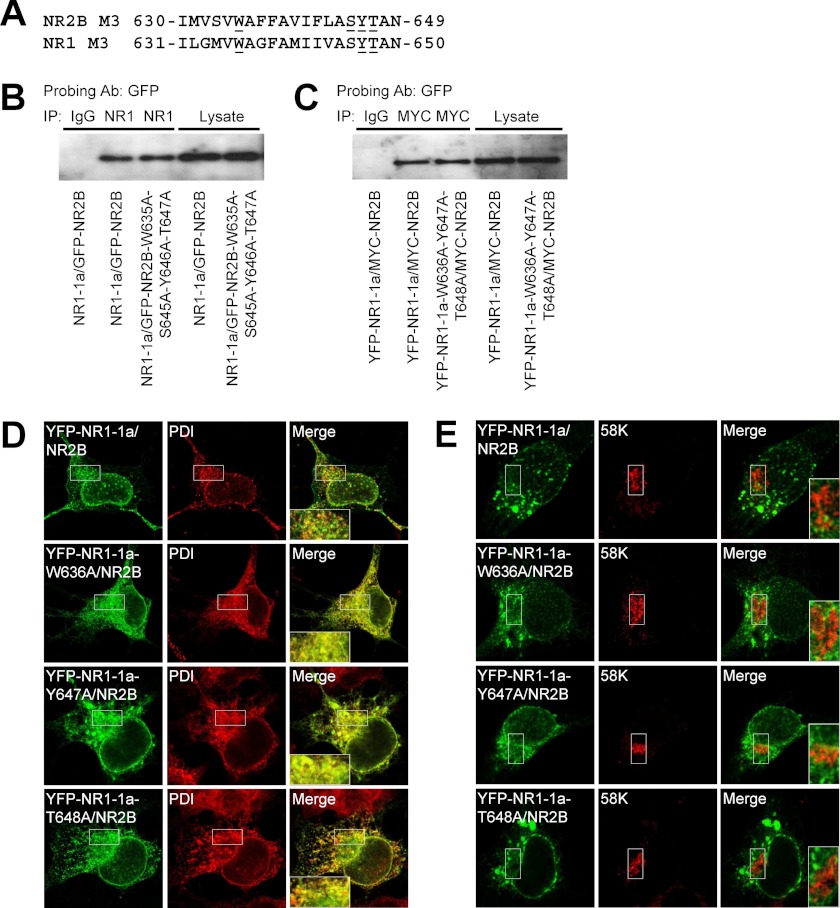
FIGURE 5.
The single alanine substitutions of the key amino acid residues within the NR2B and NR1 M3 domains contribute to the regulation of the trafficking of the functional receptors. A, the amino acid sequences of the NR2B and NR1 M3 domains are shown, and the amino acid residues replaced with alanines are underlined. B and C, COS-7 cells cotransfected with indicated NR1/NR2B subunits were solubilized with 1% deoxycholate, immunoprecipitated (IP) with mouse anti-NR1 (B) or anti-MYC (C) antibodies (Ab), and probed with rabbit anti-GFP antibody. The specificity of coimmunoprecipitation was tested by using IgG. The images show the representative results from three independent experiments. Densitometric analysis revealed no significant differences in the normalized amounts of the bound fractions among the studied combinations of the subunits (ratio between YFP-NR1-1a-W636A-Y647A-T648A/MYC-NR2B and YFP-NR1-1a/MYC-NR2B, 1.07 ± 0.12; ratio between NR1-1a/GFP-NR2B-W635A-S645A-Y646A-T647A and NR1-1a/GFP-NR2B, 1.09 ± 0.04; n = 3). D and E, the distribution of indicated mutated NMDA receptors closely matches the distribution of an ER marker (D) but not a GA marker (E). Images were taken on fixed COS-7 cells using a confocal microscope. PDI, oxidoreductase-protein disulfide isomerase.