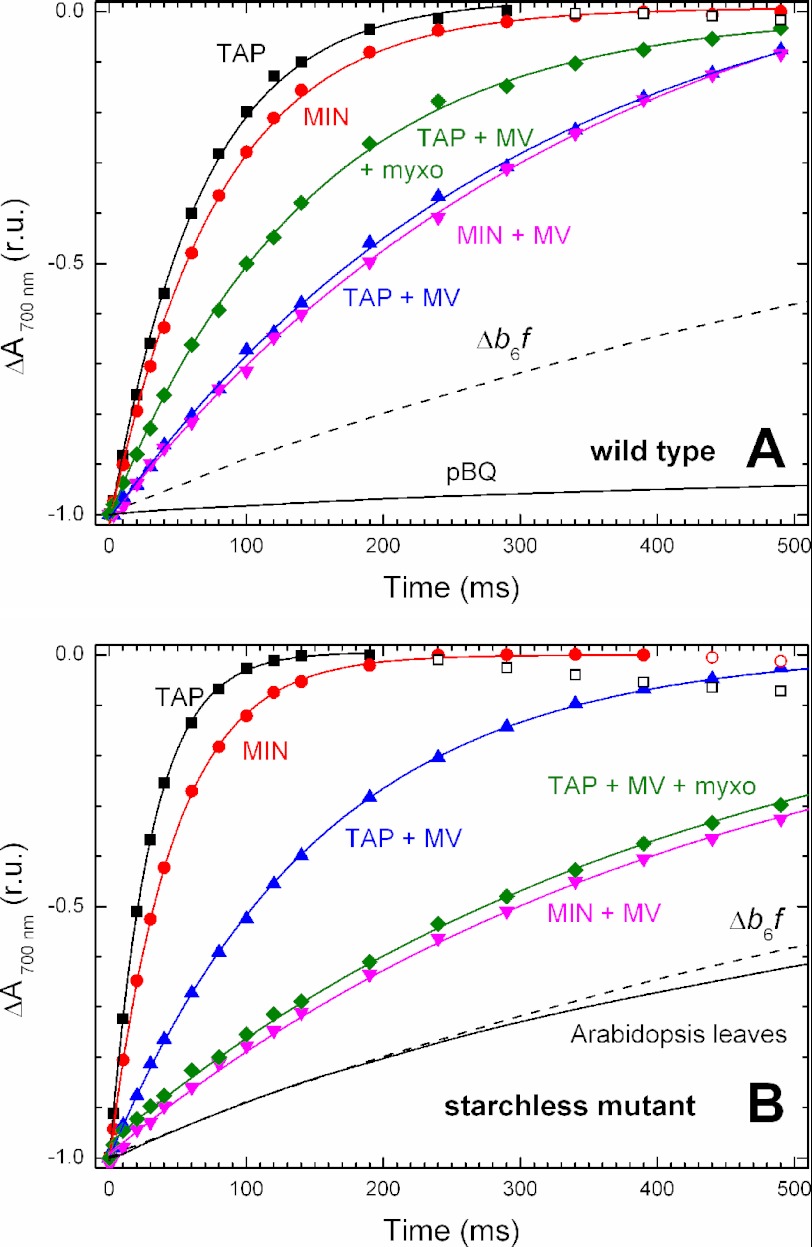
FIGURE 2.
Absorbance changes at 700 nm following 10 s of saturating light in aerobic Chlamydomonas cells. A, WT strain. B, starchless sta6 mutant. Solid symbols show the dark reduction of P700+; open symbols show the subsequent reduction of plastocyanin. Data were fitted to an exponential decay (solid line). The contribution of linear electron flow was discarded by adding 10 μm DCMU. In this case, the relaxation rate of P700 reflects the photosynthetic cyclic electron flow around PSI. In the presence of 2 mm methylviologen, cyclic electron flow is blocked, and the remaining electron flow toward P700+ is due to the NADPH produced by the cell metabolism (starch breakdown and acetate assimilation). Cells were resuspended in 10% Ficoll to avoid sedimentation and TAP or minimal (MIN) medium. Myxothiazol was used at a concentration of 20 μm to block ATP production by oxidative phosphorylation. Dashed lines show the kinetics obtained with a mutant devoid of the cytochrome b6f complex, and the solid line corresponds to cells treated with 50 μm p-benzoquinone, DCMU, and methylviologen (A), or Arabidopsis leaves treated with DCMU and methylviologen (B). See Table 1 for the average rates and S.D. r.u., renormalized units.