Figure 3.
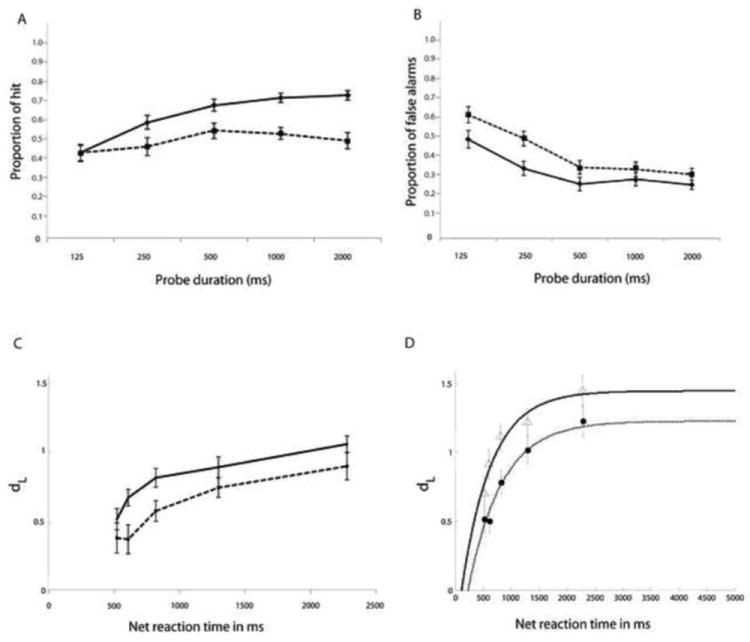
A and B Proportion of hits (A) and false alarms (B) at each probe duration in the young and old groups. C and D Calculated (C) and modeled (D) speed accuracy trade-off functions on the delayed item recognition task in the young and old groups. Data are shown for 26 young adults (solid lines) and 23 older adults (dotted lines). Error bars represent standard errors. dL = discriminability. Net reaction time is the sum of probe duration and reaction time from the onset of the response signal.
