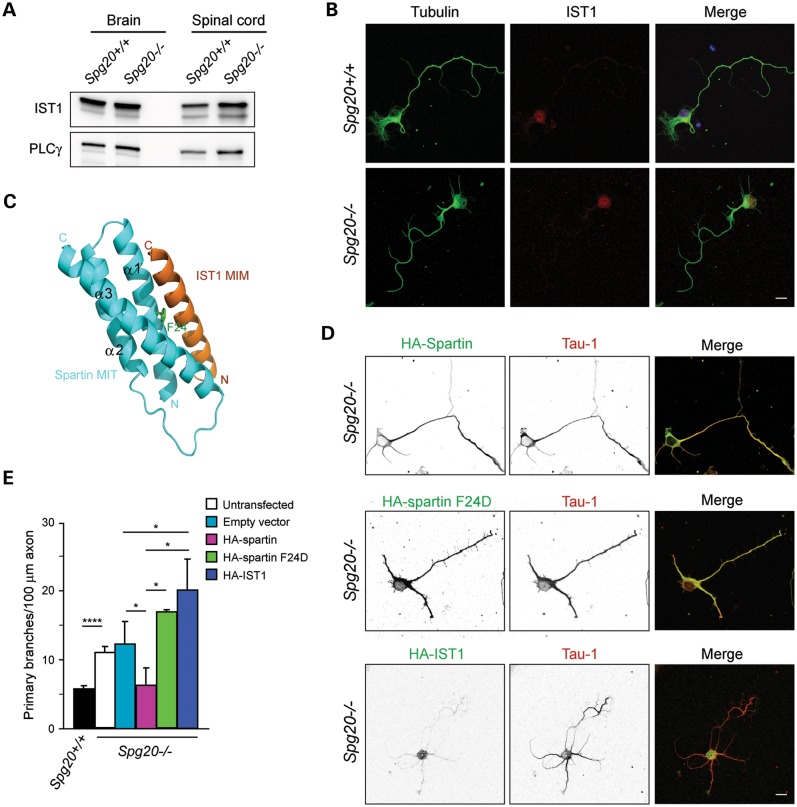
Figure 4.
Interaction with the ESCRT-III protein IST1 is required for spartin-mediated effects on axonal branching. (A) Immunoblot of IST1 protein in total lysates from brain and spinal cord of Spg20+/+ and Spg20−/− mice. PLCγ is a control for protein loading. (B) Representative cultured cerebral cortical neurons from Spg20+/+ and Spg20−/− mice stained with β-tubulin (green) and IST1 (red). Scale bar, 20 µm. (C) Structural model of spartin MIT domain (blue) interacting with IST1 MIT-interacting motif (MIM; orange). Residue Phe24 (F24) in the spartin MIT domain is shown in green. Adapted from ref. 21. (D) Spg20−/− neurons overexpressing wild-type HA-spartin, HA-spartin F24D or HA-IST1 were co-stained with HA-tag (green) and Tau-1 (red) antibodies. Black and white images are at the left, and merged color images are to the right. Scale bar, 20 µm. (E) Quantification of number of branches per 100 µm of axon in DIV3 cortical neurons, transfected as indicated (n = 3, with 30 neurons per trial). The genotype is shown below. *P < 0.005, ****P < 0.001.