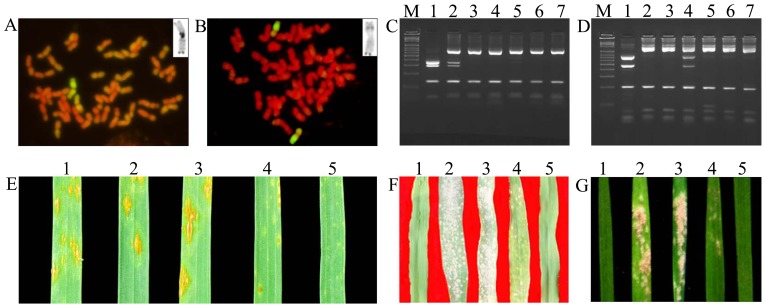
Fig. 1.
Cytological, molecular and disease resistance test results from wheat-D. breviaristatum addition lines: A and B: GISH of wheat-D. breviaristatum addition lines Y93-1-6-6 (A) and Y93-1-A6-4 (B). The top right corners of the figures are the target D. breviaristatum chromosome C-banding patterns, which were the same as Vb1 and Vb5, respectively, from Fig. 2 in Yang et al. (2008). The scale bar is 20 μm. C and D: STS-PCR patterns for D. breviaristatum (1), Y93-1-6-6 (2), Longfu 10 (3), Y93-1-A6-4 (4), 99E-18 (5), ML19 (6) and CS (7), respectively using BE404728-F, BE404728R (C) and BE517627-F, BE517627 (D) as primer pairs. PCR products were cut by RsaI (C) and HaeIII (D) separately. M, Marker (DL2000). E: Infection types produced by wheat-D. breviaristatum addition lines Y93-1-A6-4 (1), Y93-1-6-6 (4) and their parents Longfu 10 (2), ML19 (3) and TDH-2 (5) when inoculated with Pgt race Ug99. F and G: Infection types produced by TDH-2 (1), ML19 (2), Longfu10 (3), Y93-1-6-6 (4) and wheat-D. villosum 6AL/6VS translocation line (5) when inoculated with mixed Sichuan (F) and mixed Kansas (USA) Bgt races (G) on adult plants.