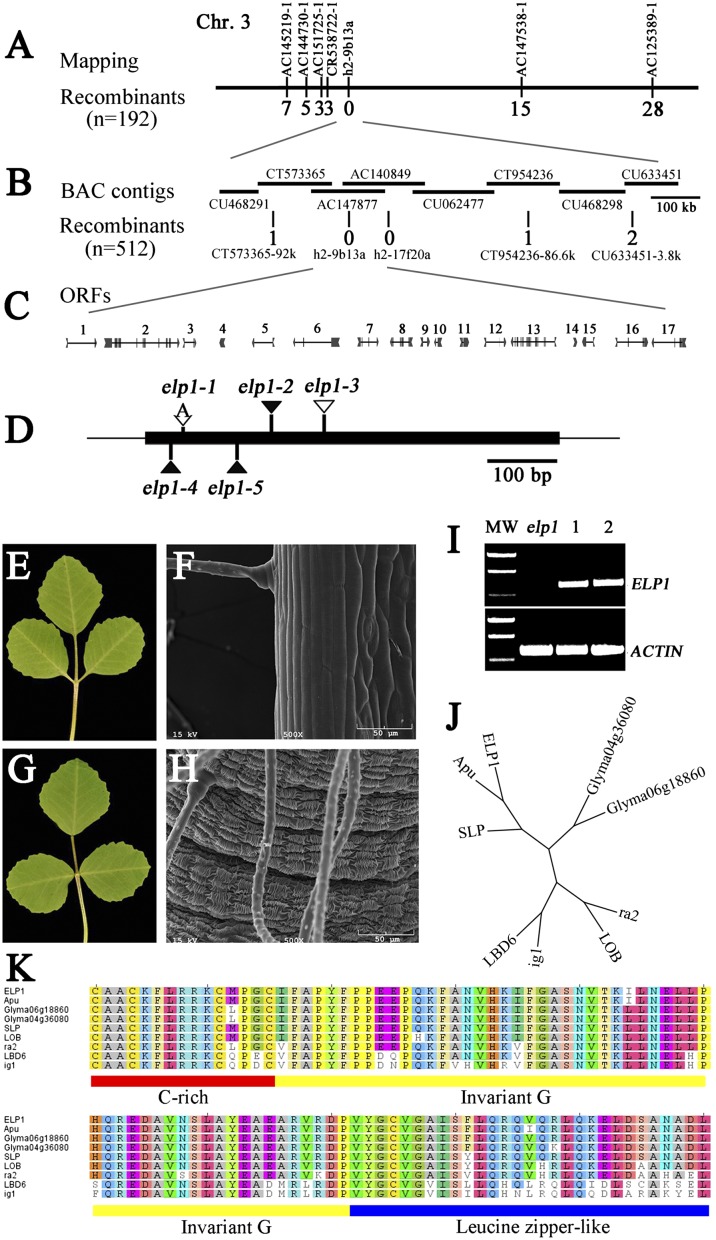
Fig. 2.
Map-based cloning, genetic complementation, and phylogenetic analysis of the M. truncatula ELP1 gene. (A) The elp1 locus was mapped to the lower arm of chromosome 3 and tightly linked to the SSR marker h2-9b13a. (B) Fine genetic mapping using a large F2 population further narrowed the elp1 map position. Horizontal lines represent BAC contigs in the mapped region. The number of recombinants with respect to elp1 is provided below each marker in A and B. (C) Predicted genes and gene structures in the mapped region. (D) Mutation sites in ORF4 identified in elp1 mutant alleles. (E–H) Genetic complementation of elp1-3. Shown are representative elp1-3 mutant trifoliate leaf (E) and SEM image of the base of a leaflet (F) and representative trifoliate leaf (G) and SEM image of the base of a leaflet (H) of the elp1-3 mutant transformed with 35S:GFP-ELP1. (I) RT-PCR analysis of ELP1 expression. MW, molecular weight markers; elp1, elp1–3; lanes 1 and 2, two independent transgenic lines in which ELP1 gene expression was restored. M. truncatula ACTIN gene was used as a loading control. (J) Phylogenetic relationship analysis of ELP1 and its closely related homologs, Apu from pea (P. sativum), SLP from L. japonicus, LOB (At5g63090), and LBD6/AS2 (At1g65620) from A. thaliana, Glyma04g36080 and Glyma06g18860 from soybean (G. max), and ra2 and indeterminate ig1 from maize (Zea mays). (K) Amino acid sequence alignments of N-terminal LOB domains of ELP1 and its homologs. The underlined LOB domain includes cysteine (C)-rich (red), invariant glycine (G; yellow), and leucine-zipper–like (blue) motifs.