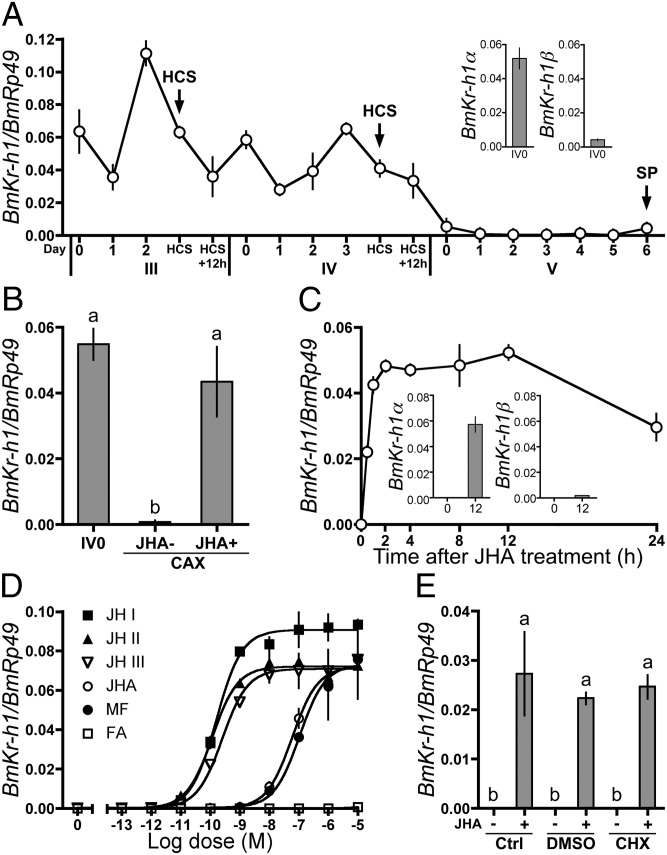
Fig. 1.
Regulation of BmKr-h1 expression by JH in B. mori larvae and NIAS-Bm-aff3 cells. BmKr-h1 expression levels were determined by qPCR. Data represent means ± SD (n = 3 except in A, where n = 2). Means with the same letter are not significantly different (Tukey–Kramer test, P < 0.05). (A) Developmental expression profiles of BmKr-h1 in the epidermis. (Inset) Expression levels of BmKr-h1α and BmKr-h1β in fourth-instar larvae at day 0. Roman and Arabic numerals under the horizontal axis indicate the instar and days in the instar, respectively. HCS, head capsule slippage; SP, spinning. (B) Effects of allatectomy (CAX) and methoprene (JHA) treatment on BmKr-h1 expression. Fourth-instar larvae at day 0 were treated with either JHA (1 μg) or acetone (JHA−) 3 h after allatectomy. Twelve hours later the epidermis was dissected, and BmKr-h1 expression was measured. (C) NIAS-Bm-aff3 cells were treated with 10 μM JHA, and temporal changes in BmKr-h1 expression were monitored. (Inset) Expression levels of BmKr-h1α and BmKr-h1β in cells treated with JHA for 0 and 12 h. (D) NIAS-Bm-aff3 cells were treated with different concentrations of JH (JH I, JH II, and JH III), JHA, MF, or FA, and the relative expression levels of BmKr-h1 were determined after 2 h. (E) Untreated cells (Ctrl) or cells precultured in a medium with 50 μM CHX or solvent only (DMSO, 3% vol/vol) for 1 h were treated with 1 μM JHA or solvent for 2 h, and the relative expression levels of BmKr-h1 were determined.