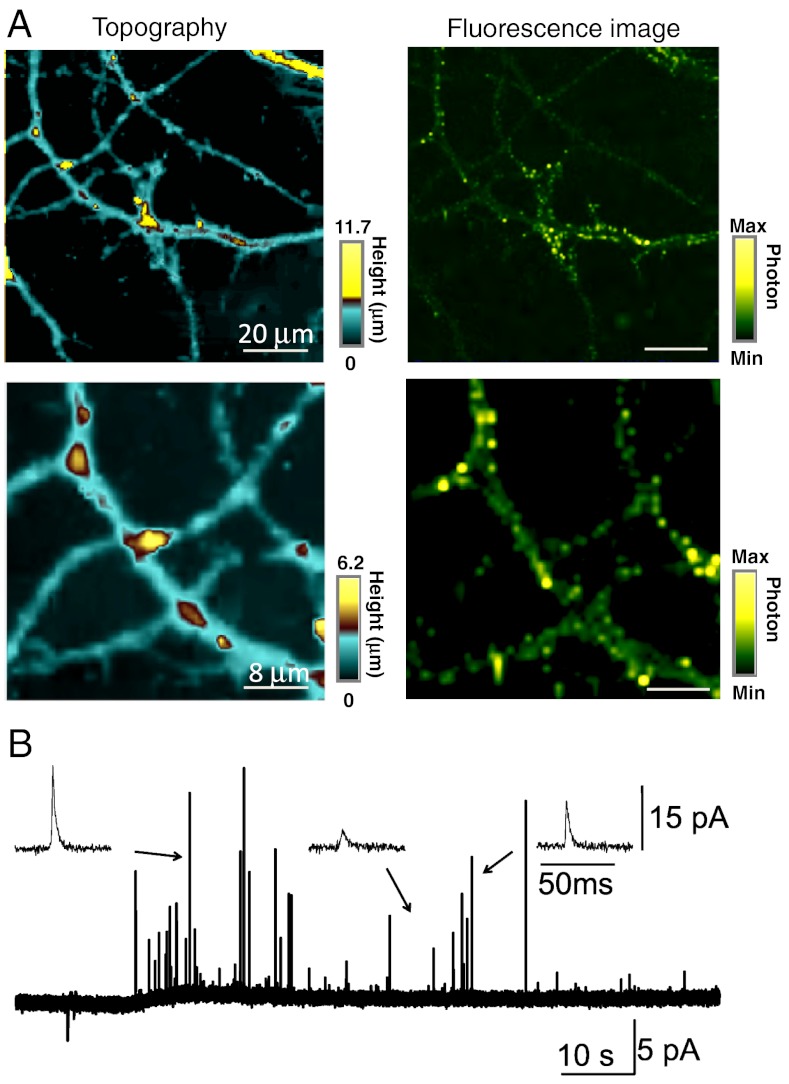
Fig. 4.
(A) Topography (Left) and fluorescence (Right) images of hippocampus neurons using constant-current mode SECM combined with confocal microscopy. The carbon electrode was held at -500 mV vs. Ag/AgCl in PBS containing 10 mM Ru(NH3)6Cl3. The electrode radius is 32.6 nm. (B) Detection of the release of the neurotransmitter using a conical-shaped carbon nanoelectrode (described in the text). A series of current spikes corresponding to neurotransmitter release detected after whole cell stimulation of 105 mM K+ using another micropipette. The carbon electrode was held at 650 mV vs. Ag/AgCl electrode. The electrode radius is 6.0 μm.