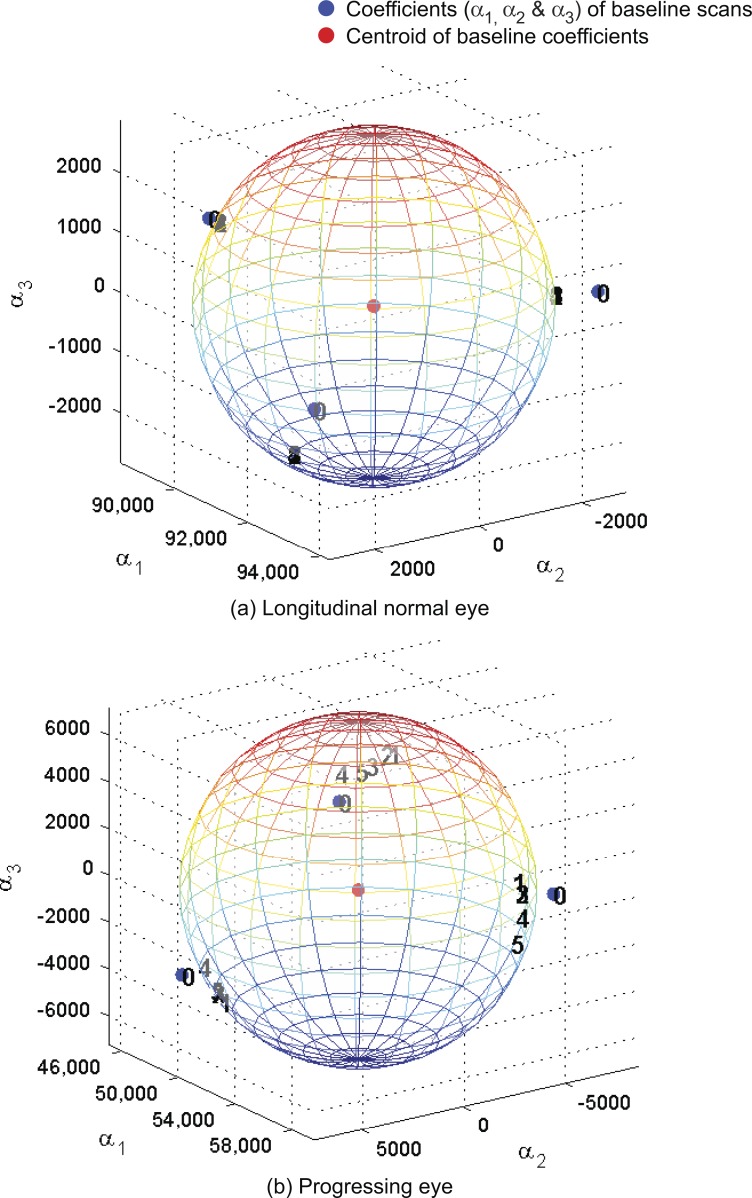
Figure A1.
Baseline subspace representation of each follow-up scan (topography) of the example normal eye (Fig. 1) and the example progressing eye (Fig. 2). Baseline subspace representations are topographic projections (with a quadratic equality constraint) of each follow-up scan on to the baseline subspace of the eye. Single topographies are represented as points in a 3-D space using their respective subspace coefficients (α1,α2,α3) with indices 0, 1, 2, and so forth. Index 0 represents the location of an observed single topography at baseline, and indices 1 and above represent the location of baseline subspace representations. Baseline topographies nearest to their respective follow-up are clustered more closely to the observed baseline topographies for the example normal eye in (a) in contrast to the example progressing eye in (b).