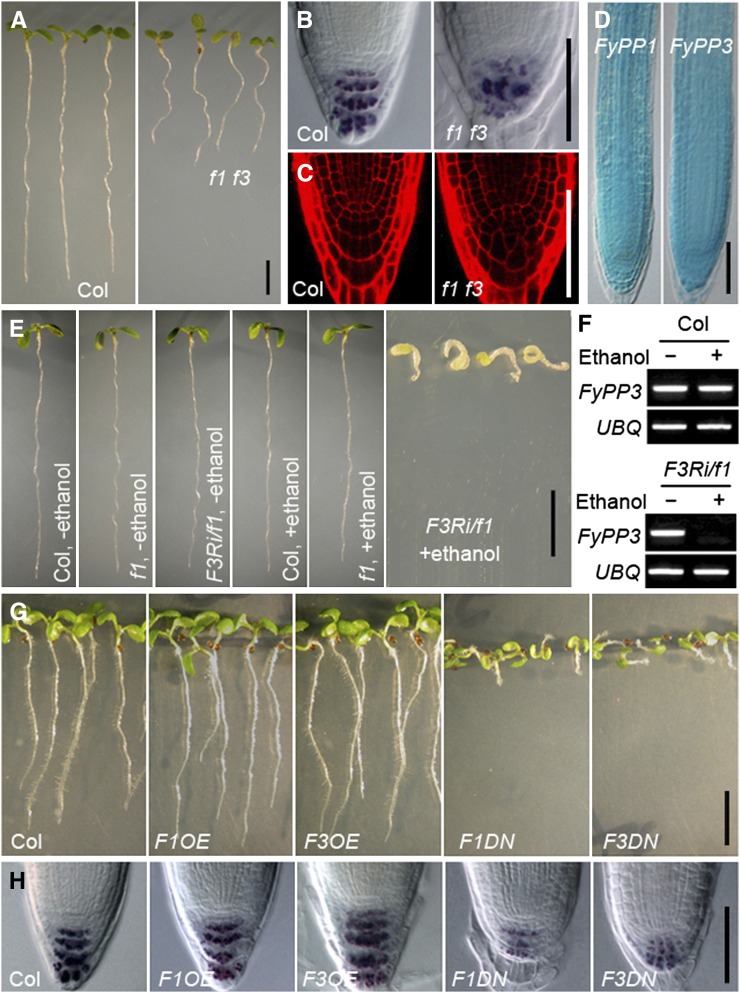
Figure 1.
Phenotypic Characterization of Root Development in f1 f3, F3Ri/f1, F1OE, F3OE, F1DN, and F3DN Plants.
(A) Shorter roots of f1 f3 double mutants versus the Col wild type. Seedlings are shown at 5 DAG. Bar = 0.5 cm.
(B) Reduced and more diffuse staining of starch granules in the root tips of f1 f3 mutants, as indicated by Lugol’s staining. Bar = 50 μm.
(C) Propidium iodide staining shows irregular cell arrangement and defective columella cells in the root tips of f1 f3 mutants. Bar = 50 μm.
(D) GUS staining shows overlapping expression patterns of FyPP1pro:GUS and FyPP3pro:GUS in primary roots. Bar = 50 μm.
(E) Developmental defects of FyPP3RNAi/fypp1 (F3Ri/f1) seedlings upon induction with ethanol. Bar = 1 cm.
(F) Silenced expression of FyPP3 gene in F3Ri/f1 plants after ethanol induction shown in (E).
(G) F1OE and F3OE roots are slightly longer than Col roots, while F1DN and F3DN roots exhibit reduced root length and agravitropism compared with Col. Seedlings are shown at 5 DAG. Bar = 1 cm.
(H) Lugol’s staining showing that the staining of starch granules is dramatically reduced in the root tips of F1DN and F3DN roots, while the staining of starch granules is largely normal in F1OE and F3OE roots compared with Col. Bar = 50 μm.