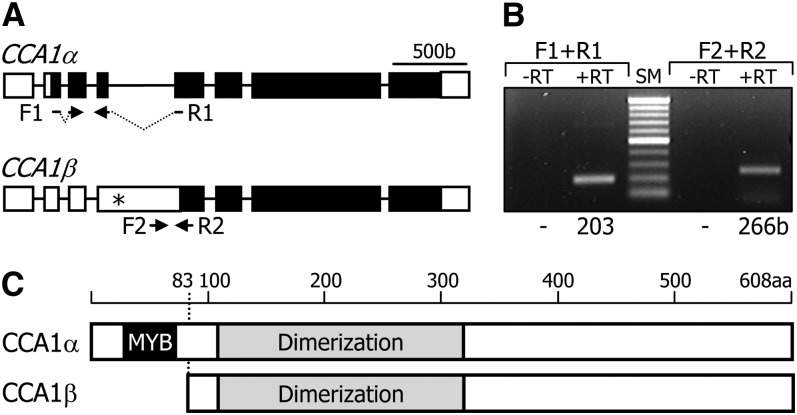
Figure 1.
Alternative Splicing of the CCA1 Gene.
(A) Genomic structure of CCA1 splice variants. White boxes indicate untranslated regions, and black boxes indicate exons. Asterisk indicates an in-frame stop codon. F1 and F2 are forward primers. R1 and R2 are reverse primers (see Supplemental Table 1 online). b, base pairs.
(B) Detection of alternatively spliced transcripts. Wild-type cDNA was subjected to RT-PCR. Sizes of the PCR products are indicated at the bottom. RT, reverse transcription; SM, size marker.
(C) Protein structures of two CCA1 isoforms. The CCA1β isoform lacks the MYB DNA binding domain. aa, amino acid.