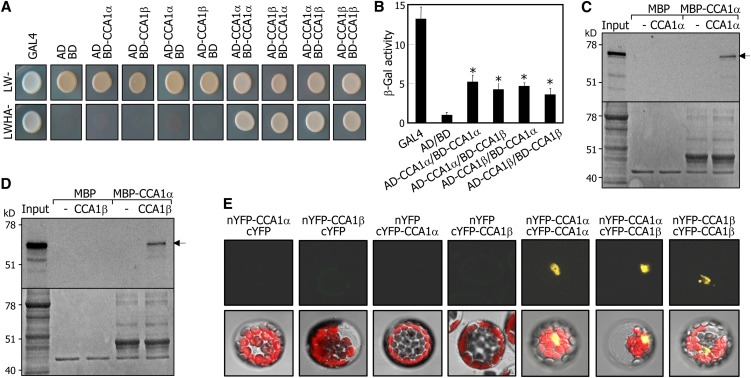
Figure 2.
Formation of Homodimers and Heterodimers of CCA1α and CCA1β.
(A) Yeast coexpression assays. Cell growth of yeast transformants on selective media without Leu, Trp, His, and Ade (LWHA-) indicates positive interactions.
(B) β-Gal activity assays in yeast cells. β-Gal activities were normalized by dividing total activity by optical cell density. Three measurements of β-Gal activities were averaged and statistically treated using a Student’s t test (*P < 0.01). Bars indicate the se.
(C) and (D) In vitro pull-down assays. A recombinant MBP-CCA1α fusion protein prepared in E. coli cells and in vitro–translated radiolabeled CCA1α (∼67 kD) (C) and CCA1β (∼58 kD) (D) were used. Arrows indicate the positions of expected bands of CCA1α and CCA1β. MBP protein was also included as a control in the assays. Bottom panels are parts of Coomassie blue–stained gels.
(E) BiFC assays. Partial YFP fusion constructs containing either CCA1α or CCA1β were transiently coexpressed in Arabidopsis protoplasts. Vectors without CCA1 genes (cYFP and nYFP) were also included in the assays. Chloroplasts appear red.