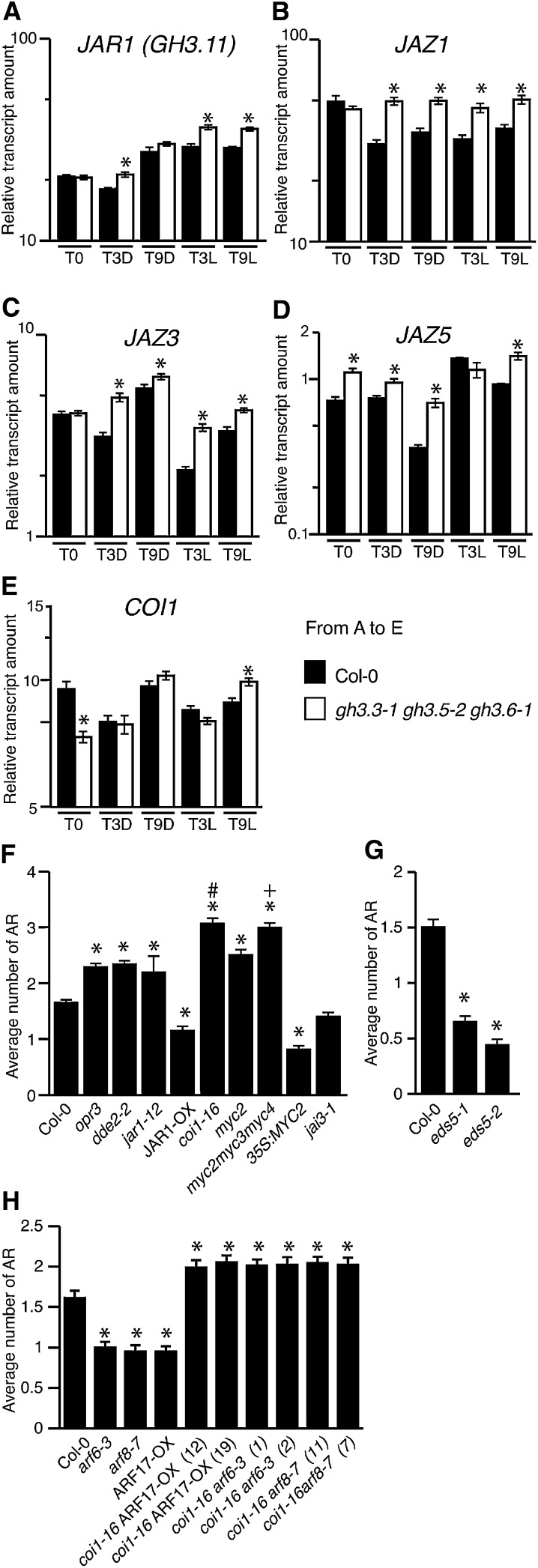
Figure 5.
The COI1 Signaling Pathway Is Required for the Inhibition of Adventitious Rooting by Jasmonate.
(A) to (E) Quantification by quantitative RT-PCR of JAR1 (GH3.11) JAZ1, JAZ3, JAZ5, and COI1 transcripts in hypocotyls of wild-type etiolated seedlings (T0), after an additional 3 or 9 h in the dark (T3D or T9D), and after transfer to the light for 3 or 9 h (T3L or T9L). Values are relative to the expression level of APT1, which was used as a reference gene as described in Methods. Error bars indicate se obtained from three independent biological replicates. A one-way analysis of variance combined with the Tukey’s multiple comparison posttest confirmed that the differences between the wild type and the mutants (*) are significant (P < 0.05, n = 3). Col-0, ecotype Columbia.
(F) and (G) Average number of adventitious roots (AR) in several mutants altered in jasmonate biosynthesis or signaling (F) and in the SA-deficient mutant lines eds5-1 and eds5-2 (G). Data from three independent biological replicates, each of at least 30 seedlings, were pooled and averaged. Error bars indicate se. A one-way analysis of variance combined with the Tukey’s multiple comparison test showed that the values indicated by asterisks are significantly different from wild-type values (P < 0.01; n > 90); the Bonferroni posttest indicates that the value indicated by the plus sign is significantly different from that of the myc2 mutant and that indicated by the hash mark is significantly different from that of jar1-12 (P < 0.01; n > 90).
(H) Average number of adventitious roots in single arf6-3 and arf8-7 mutants and the ARF17-OX line and in the corresponding double mutants with coi1-16. Data from three independent biological replicates, each of at least 30 seedlings, were pooled and averaged. Error bars indicate se. A one-way analysis of variance combined with the Dunnett’s multiple comparison test showed that the values indicated by asterisks are significantly different from wild-type values (P < 0.05; n > 90).