Figure 1.
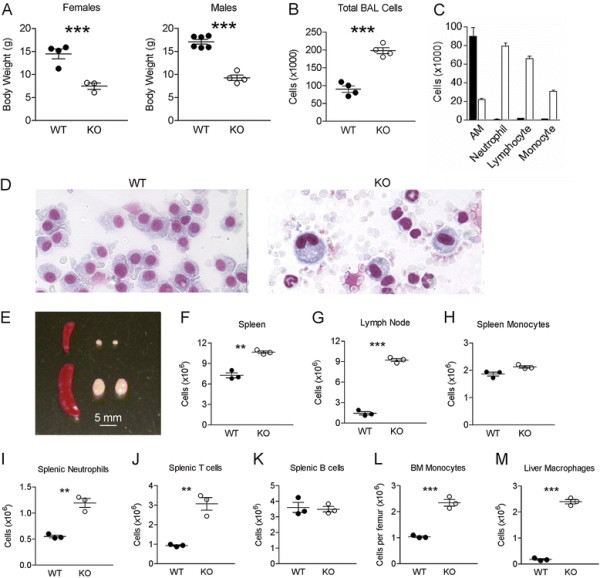
Mice lacking TβRII in hematopoietic cells develop a lethal inflammatory and autoimmune syndrome. (A) Body weight of male and female Vav-Cre x TβRIIfx/fx(TβRII-/-) mice and littermate controls at postnatal day 18-21. (B) Total cell counts and (C) differential cell counts in BALF of WT and TβRII-/- mice at postnatal day 18-21. Solid bar, WT; Open bar, TβRII-/- samples. Differences are significant (p < 0.01) for all cell populations in panel C. (D) Wright-Giemsa-stained BALF cells from the indicated genotypes (18-day old littermates). Note the presence of a single cell type - the alveolar macrophage - in the control lung, whereas the TβRII-/- sample contains neutrophils, monocytes and lymphocytes. (E) Photographic images of spleens and lymph nodes; total cell counts in (F) spleens and (G) lymph nodes; total numbers of (H) monocytes, (I) neutrophils, (J) T-cells and (K) B-cells in spleen; total counts of bone marrow monocytes (L) and liver macrophages (M) in WT (filled circles)and TβRII-/- (KO, open circles) mice (n = 3, **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).
