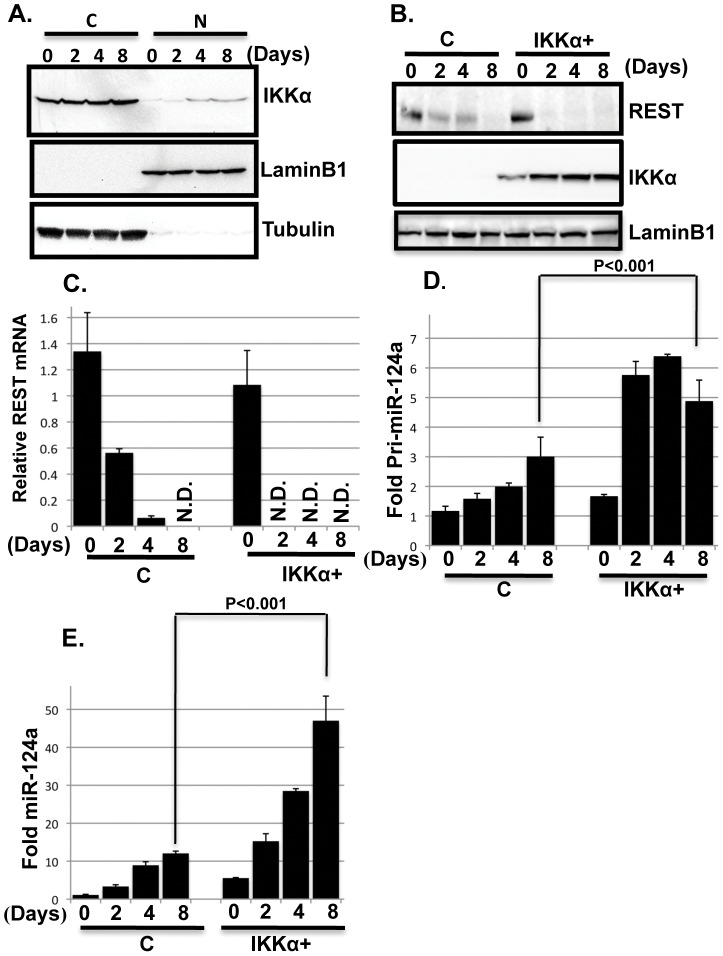
Figure 4. IKKα regulates REST and miR-124a expression.
(A) IKKα accumulates in the nuclei of differentiating MESC2.10 NPCs. Representative Western blot results for levels of endogenous IKKα in the cytoplasm (C) and nuclear (N) fractions of differentiating NPCs (top panel) are shown. IKKα was detected with a mouse anti-IKKα antibody. Nuclear LaminB1 and cytoplasmic tubulin were used as loading controls (middle and bottom panels, respectively). (B) REST protein levels also decline faster in differentiating IKKα+ NPCs compared to differentiating controls. Representative western blot results are shown from nuclear lysates for REST (top panel), IKKα (middle panel) and laminB1 (bottom panel). REST was detected with a mouse anti-REST antibody and Anti-Flag antibody was used to detect IKKα. LaminB1 was used a as loading control. (C) After initiating differentiation, REST mRNA levels decline faster in IKKα+ NPCs than in control cells. Taqman probes were used to quantify the mRNA levels at the days shown. The data are shown relative to the level in proliferating control NPCs. GAPDH mRNA was used for normalization. Triplicate samples were averaged for each point, and the SEMs indicated. N.D., not detected. (D, E) The accumulation of primary (pri-miRNA) and mature miRNA-124a are shown in D and E, respectively. Taqman probes were used for the qPCR. Pri-miRNA was normalized to GAPDH mRNA and mature miRNA was normalized to the small RNA, RNU6. The data are shown relative to the levels in proliferating control NPCs. P values were obtained using student's t-test.