Figure 3. Deletion breakpoints in patients A37 and A39 localize to Alu elements and display microhomology.
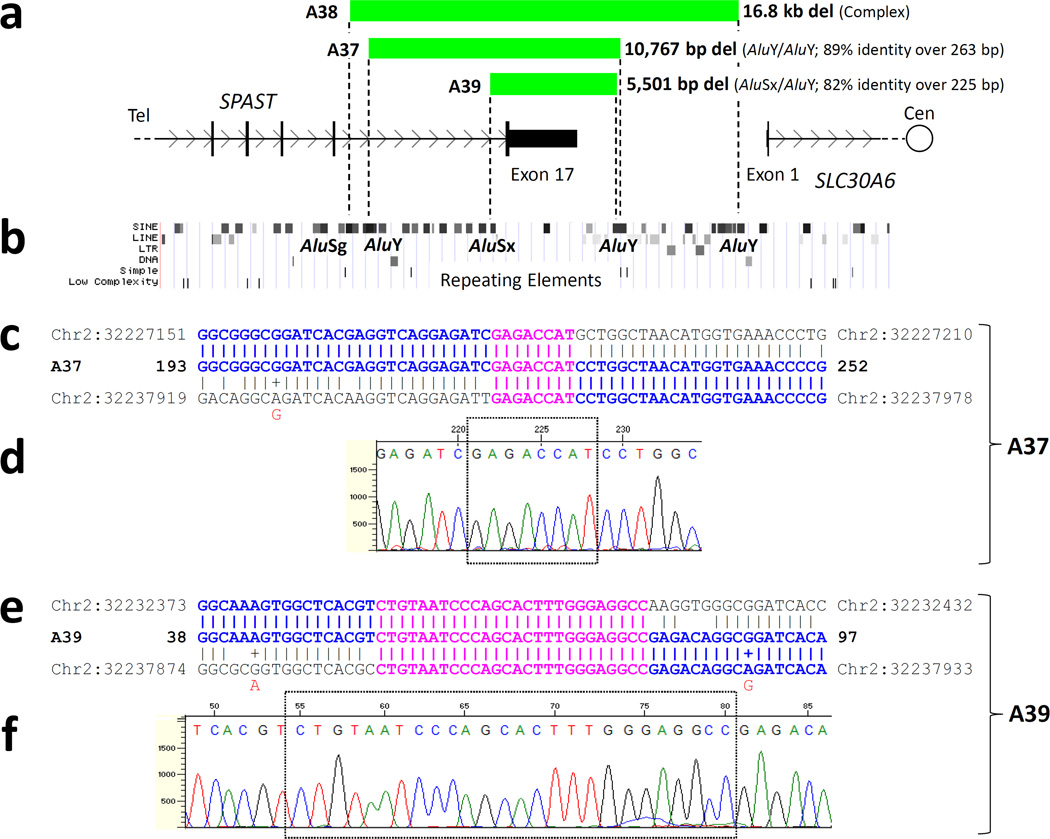
a. Green bars represent the regions deleted in patients A37, A38, and A39, superimposed on a genomic map of the 3’ end of SPAST. In each case, only exon 17 is deleted. b. A map of repeating elements, obtained from the UCSC genome browser (http://genome.ucsc.edu/) is aligned with [a]. All deletion breakpoints (indicated by dotted lines in [a]) fall within Alu elements; each pair of Alus flanking a deletion are in direct orientation with each other. (c–f). Sequencing of the breakpoint regions in patients A37 and A39 reveals microhomology. c and e. The DNA sequences of the deletion breakpoint regions of mutant patient chromosomes (“A37” and “A39”) are displayed between the telomeric (top) and centromeric (bottom) reference sequences. Perfect sequence identity with one of the reference sequences is indicated with bold blue text. Microhomology (sequence identity among all three sequences) is indicated with bold pink text. A “+” and red lettering indicate a known SNP, as listed by the UCSC genome browser, which matches the sequenced patient DNA. d and f. DNA sequencing traces. The regions of microhomology are boxed. Though the centromeric breakpoints of patients A37 and A39 fall within the same AluY element, their exact locations differ. Del, deletion; cen, centromeric; tel, telomeric.
