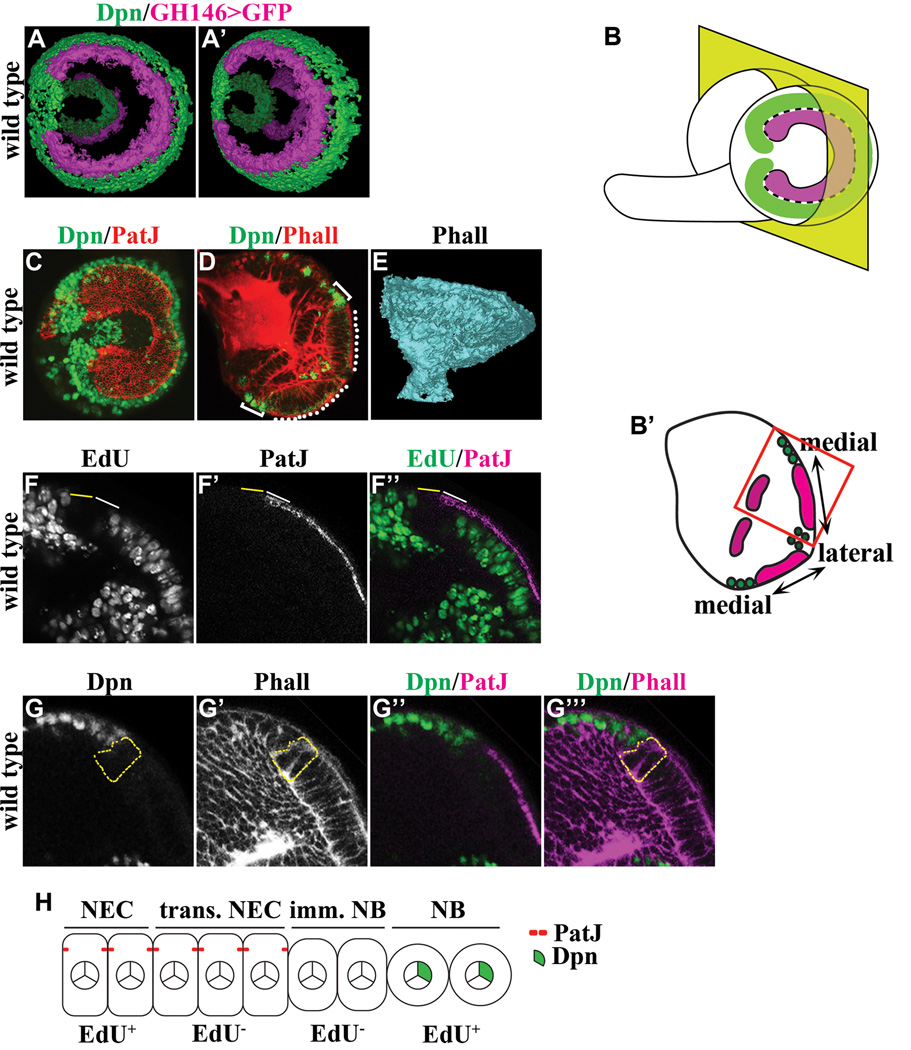
Figure 1. Identification of intermediate cell types during differentiation of neuroepithelial cells into neuroblasts.
(A–A’) Three-dimensionally reconstructed views of the outer and inner proliferation center in the third larval instar optic lobe. The expression of GH146-Gal4 marks neuroepithelia in the outer (bright colored) and inner (faded colored) proliferation center whereas expression of Deadpan (Dpn) marks neuroblasts.
(B–B’) Visualization of the developing larval optic lobe. (B) A lateral projection view of a wild type larval optic lobe shows the overall morphology of the outer proliferation center, which consists of a C-shape swath of neuroepithelia (magenta) surrounded by neuroblasts (green). The medial edge of neuroepithelia separating neuroepithelial cells and neuroblasts is indicated by the black & white dotted line. (B’) A dorsoventral single confocal optical section of a wild type larval brain (as indicated by the yellow plane in B) reveals neuroepithelia in the inner and outer proliferation center. In this view, optic lobe neuroblasts flank the medial edge of neuroepithelia in the outer proliferation center. The higher magnification image of neuroepithelia and neuroblasts boxed in red is used in subsequent figures to illustrate the effects of removing or increasing the function of a gene.
(C) The lateral projection view of a wild type larval optic lobe stained for PatJ and Dpn reveals the swath of neuroepithelia flanked by neuroblasts.
(D) A dorsoventral single confocal optical section of a wild type larval brain stained for Phalloidin (Phall) and Dpn shows neuroepithelia in the outer proliferation center (white dotted line) flanked by neuroblasts (white bracket).
(E) A three-dimensionally reconstructed model of a wild type optic lobe stained for Phall reveals the axon bundles that constitute the neuropil.
(F–F’’) Differentiating neuroepithelial cells and immature neuroblasts are transiently arrested in cell cycle. Transitioning neuroepithelial cells (solid white line) located at the medial edge of neuroepithelia and the adjacent immature neuroblasts (solid yellow line) do not incorporate EdU following a 3-hour pulse labeling. The area shown corresponds to the red box in B’.
(G–G’’’) Immature neuroblasts do not maintain the epithelial cell morphology and do not express the neuroblast marker. Immature neuroblasts (outlined in dotted yellow line) located immediately adjacent to transitioning neuroepithelial cells lack expression of PatJ and Dpn. The area shown corresponds to the red box in B’.
(H) A cartoon summarizes the intermediate cell types during conversion of neuroepithelia into neuroblasts. NEC: neuroepithelial cells; trans. NEC: transitioning neuroepithelial cells; imm. NB: immature neuroblast; NB: neuroblast.