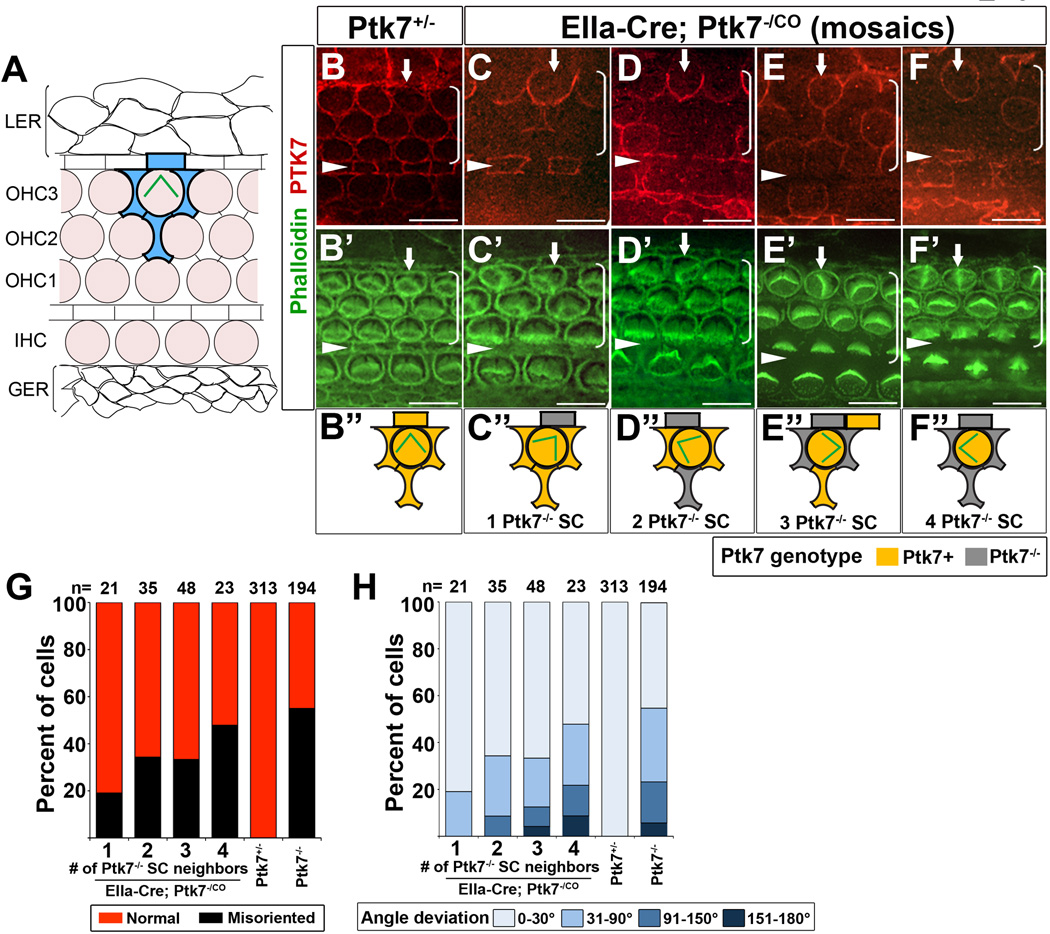
Figure 3. Mosaic analysis of Ptk7 in hair cell PCP.
(A) Schematic diagram of cellular organization in the OC. Hair cells (shaded light pink) are separated from one another by intervening supporting cells. Each hair cell in OHC3 is immediately surrounded by four supporting cells (shaded in blue). Flanking the OC are cells of the lesser epithelial ridge (LER) and the greater epithelial ridge (GER). (B–F”) Mid-basal region (25% cochlear length) of E18.5 cochleae stained with PTK7 antibodies (red) and phalloidin (green). (B, B’) In controls, PTK7 is expressed in both hair cells and supporting cells and localized to cell-cell contacts. (C-F”) Examples of Ptk7 mosaics in EIIa-Cre; Ptk7−/CO cochleae. Ptk7+ hair cells with misoriented stereociliary bundles (arrows) surrounded by different numbers of Ptk7−/− supporting cells (SC) are shown and schematized. (G, H) In EIIa-Cre; Ptk7−/CO mosaic cochleae, both the penetrance (G) and the severity (H) of bundle orientation defects in Ptk7+ OHC3 positively correlates with the number of Ptk7−/− supporting cell neighbors. Arrowheads indicate the row of pillar cells. Brackets indicate OHC rows. Lateral is up in all micrographs. Scale bar: 10 μm. (See also Figure S3).