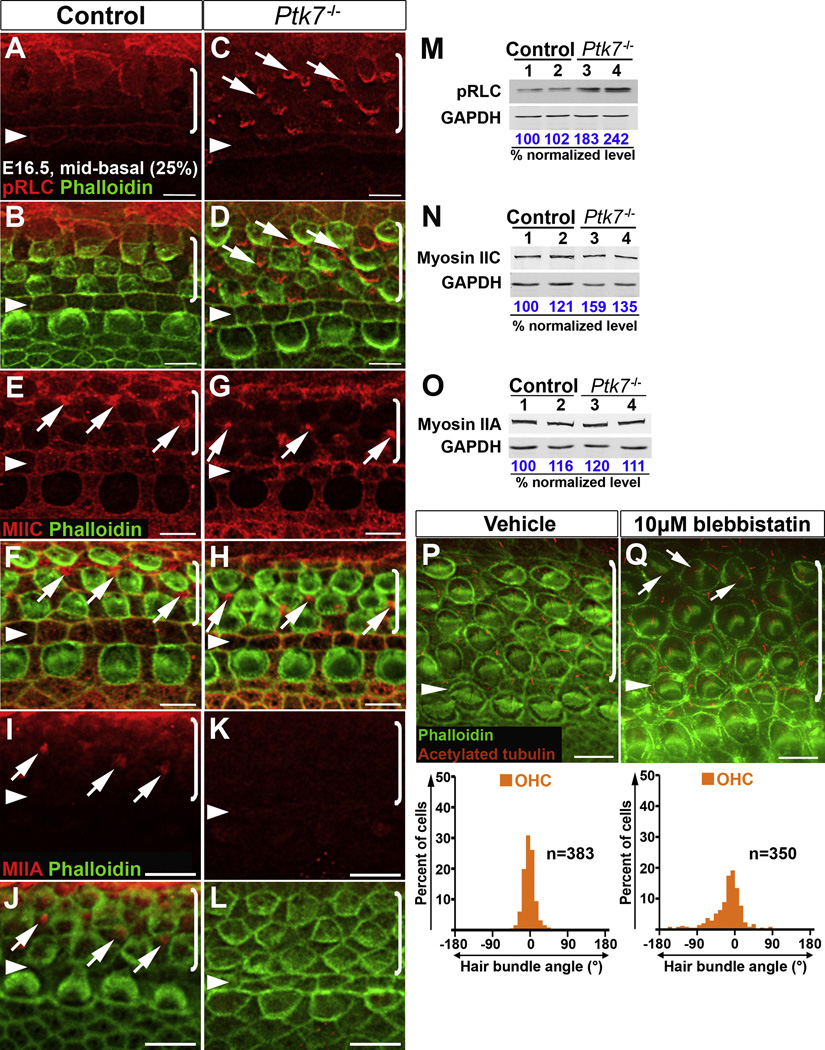
Figure 6. Ptk7 regulates myosin II activity to orient hair cell PCP.
(A–L) Localization of pRLC (A–D), MIIC (E–H) and MIIA (I–L) in the mid-basal region of OC (25% cochlear length) at E16.5. Green, phalloidin staining. (A, B) In the control, pRLC (red) is localized to cell-cell contacts. (C, D) In Ptk7−/− OC, pRLC staining was decreased at cell boundaries but increased in apical foci in supporting cells (arrows). (E, F) In the control, MIIC (red) localizes to cell-cell contacts and apical foci in supporting cells (arrows). (G, H) In Ptk7−/− OC, MIIC staining was reduced at cell boundaries but still localized to apical foci in supporting cells (arrows). (I, J) In the control, MIIA (red) is localized to apical foci in supporting cells (arrows). (K, L) In Ptk7−/− OC, MIIA staining was undetectable. (M–O) Western blot analysis of total levels of pRLC, MIIC and MIIA in E16.5 Ptk7−/− cochleae. Lysates from four cochleae of the same genotype were pooled and loaded in each lane. GAPDH served as loading control. Numbers on the bottom indicate percentage of normalized levels. (P, Q) Phalloidin (green) and acetylated-tubulin (red) staining of cochlear explants treated with either vehicle (P) or 10 µM blebbistatin (Q), with quantification of bundle orientation shown beneath. Arrows indicate examples of misoriented stereociliary bundles in blebbistatin-treated explants. Arrowheads indicate the row of pillar cells. Brackets indicate OHC rows. Lateral is up in all micrographs. Scale bars, A–H, 5 µm; I–L, P–Q, 6 µm.