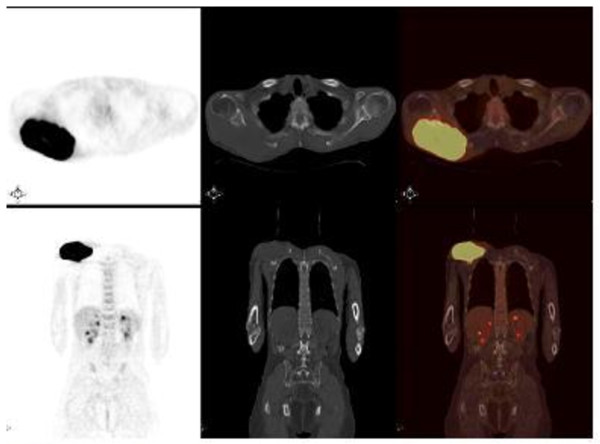
Figure 1.
Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography. The patient was intravenously injected 455 MBq (12.3 mCi) of F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose after 6 hours of fasting. After one hour of waiting time in a silent room, the patient was imaged using an integrated positron emission tomography-computed tomography camera, which consists of a six-slice computed tomography gantry integrated on a lutetium oxyorthosilicate-based fullring positron emission tomography scanner (Siemens Biograph 6, IL, USA). (A) Anterior-posterior maximum intensity projection positron emission tomography image; (B) axial positron emission tomography and (D) axial fusion images show intense hypermetabolic mass with a maximum standard uptake value (SUVmax) of 15.2 at the level of infraspinatus muscle in the right posterior shoulder. (C) Axial computed tomography image shows a soft tissue mass destructing the right scapula in the right posterior shoulder. Maximum intensity projection image shows another focus of fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the midline of the upper pelvis.