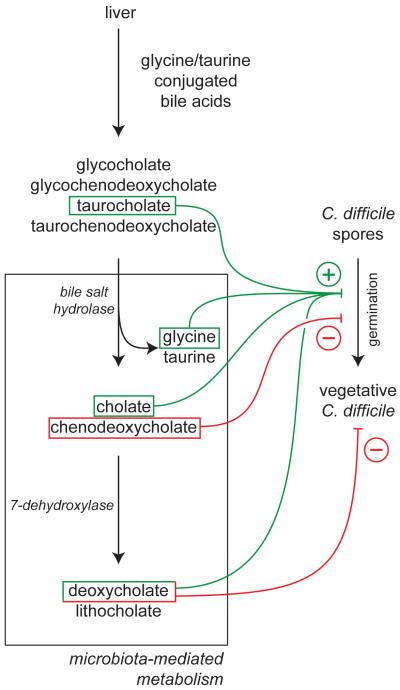
Figure 2.
Bile acid metabolism and C. difficile. Conjugated bile salts produced by the liver are metabolized in the intestine, primarily by activities carried out by members of the gut microbiota. Primary bile salts as well as their metabolites can have direct effects on C. difficile, primarily affecting germination of spores as well as the activity of vegetative cells. The balance of the positive and negative effects on C. difficile, which in turn reflect the overall community structure of the gut microbiota, may determine the ultimate clinical outcome of C. difficile exposure.