FIGURE 8.
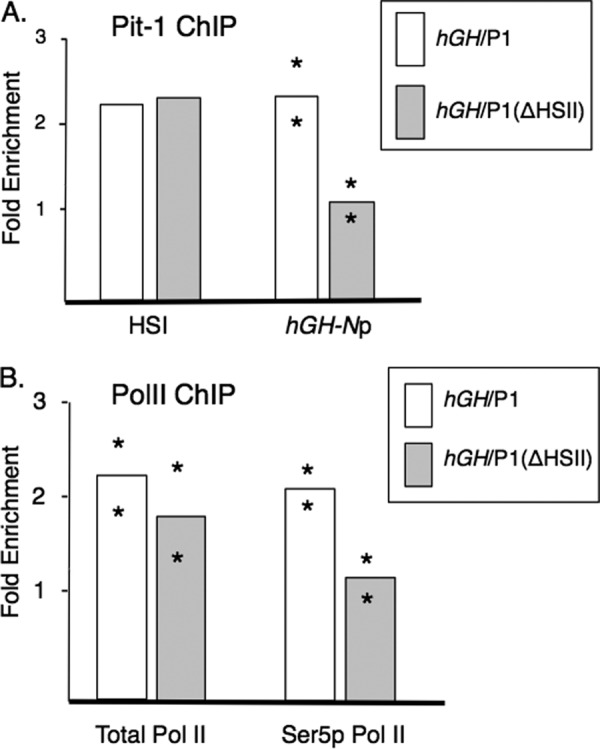
Deletion of HSII resulted in significant loss of Pit-1 recruitment and selective decrease in the phosphorylated Ser-5 isoform of PolII at the hGH-N promoter. A, ChIP was performed on pituitary chromatin from hGH/P1 or hGH/P1(ΔHSII) transgenic mice using an antibody that was raised against full-length Pit-1 protein. The fold-enrichment was calculated as antibody signal over the IgG background, normalized to the signal at myoD, an inactive promoter. Two lines were tested for enrichment at the hGH-N promoter, and one line was assayed for enrichment at HSI. All mice analyzed were compound transgenics carrying the indicated hGH transgenes and a transgene overexpressing hGRF. Bar heights represent averages, with asterisks indicating individual results from independent lines. Note that Pit-1 was decreased at the hGH-N promoter but not at HSI. B, deletion of HSII from the hGH transgene locus resulted in decreased occupancy by the elongation-competent isoform of RNA polymerase II (Ser5p PolII) at the hGH promoter. ChIP was performed against total RNA polymerase II (left) and with an antibody that is selective to PolII phosphorylated at Ser-5 of the CTD (right). Mice that were compound transgenic for the noted hGH transgene along with the hGRF transgene were assayed. Calculation and notation are the same as in Fig. 7.
