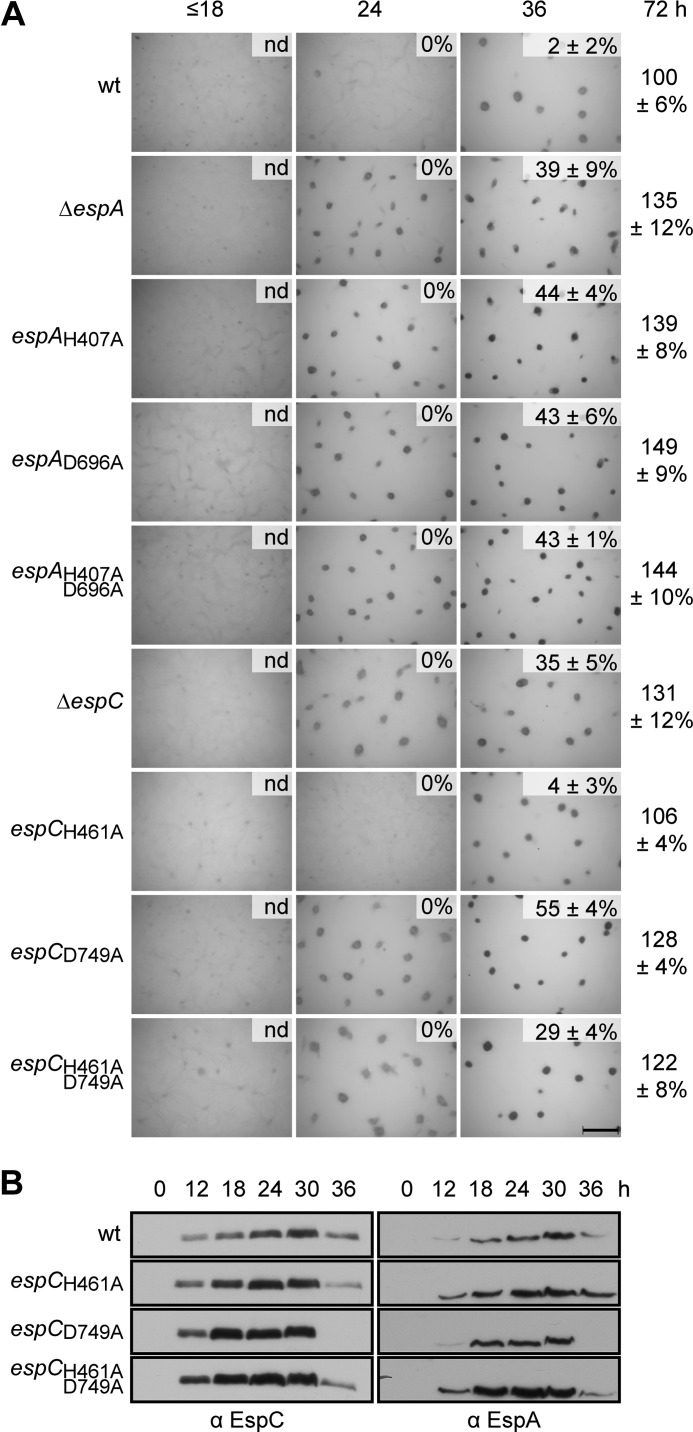
FIGURE 3.
Phosphorylation of EspC receiver domain, but not EspC autophosphorylation, is required for regulation of development. A, developmental phenotypes of espA and espC signal transmission point mutants. Wild type (wt; DZ2), ΔespA (DZ4227), espAH407A (PH1008), espAD696A (PH1009), espAH407A,D696A (PH1029), ΔespC (PH1044), espCH461A (PH1026), espCD749A (PH1027),and espCH461A,D749A (PH1028) strains were developed under submerged culture in 24-well culture dishes, and pictures were recorded at the indicated hours of development. Heat- and sonication-resistant spores were isolated at the indicated time points and displayed as the percent of wild type spores at 72 h. Spore numbers are the average and associated standard deviation of three biological replicates. Scale bar, 0.5 mm; nd, not determined. B, EspC and EspA developmental protein accumulation patterns. Anti-EspC (left panel) and anti-EspA (right panel) immunoblot analyses of cell lysates were prepared from the indicated strains developed for the indicated hours under 16 ml of submerged culture format.