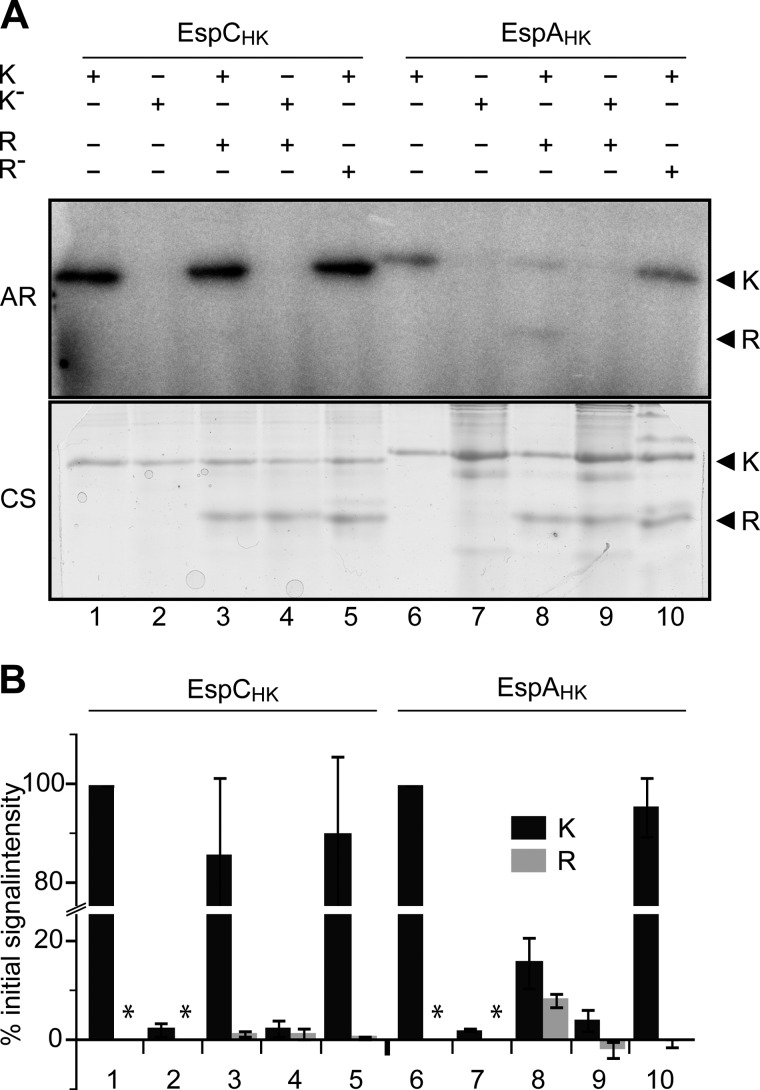
FIGURE 5.
EspAHK, but not EspCHK, efficiently phosphorylates EspCREC. A, in vitro phosphotransfer from autophosphorylated EspC or EspA kinase regions to EspC receiver domain (EspCREC). Lanes 1–5, EspCHK-His6 (K) or EspCHK H461A-His6 (K−) was first incubated in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP for 30 min and then incubated with either buffer or equimolar (10 μm) EspCREC-His6 (R) or EspCREC D749A-His6 (R−) for 2 min as indicated. +, indicated component present; −, indicated component absent. Lanes 6–10, EspAHK-His6 (K) or EspAHK H407A-His6 (K−) analyzed as per lanes 1–5. All samples were quenched and resolved by SDS-PAGE, and radiolabel was detected by exposure to a Storage PhosphoScreen (AR). Total protein was subsequently detected by Coomassie stain (CS). B, quantification of the relative signal intensities of radiolabeled EspC or EspA HK (K, black bars), and EspCREC (R, gray bars). Signal intensities are the average and associated standard deviation of three biological replicates of the reactions represented in A. HK and REC intensity values are reported as a percent of the respective Esp HK autophosphorylation controls (represented by lanes 1 and 6, respectively). *, not determined.