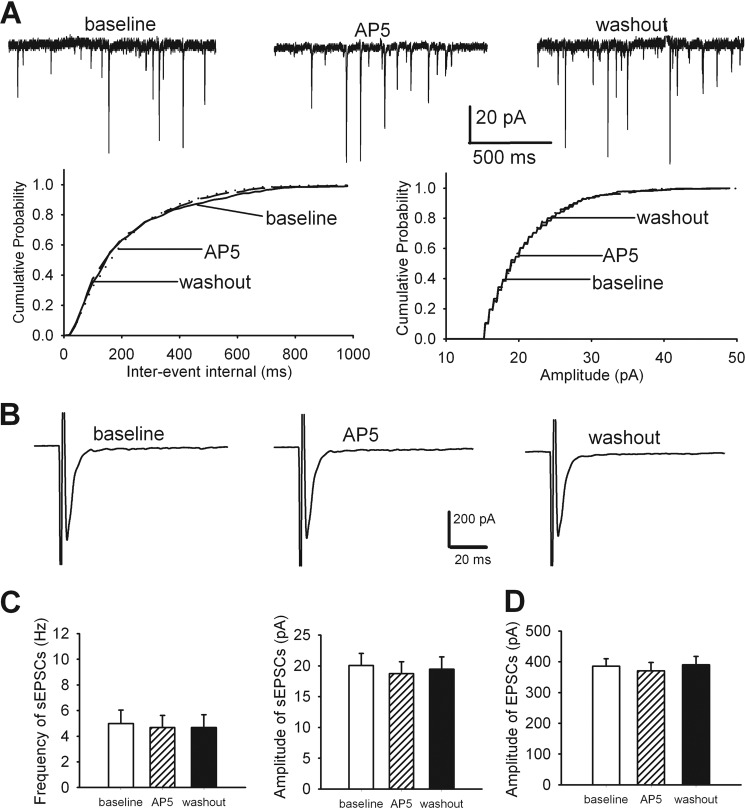
FIGURE 4.
PKC contributes to augmented glutamatergic input to spinal dorsal horn neurons induced by chronic morphine. A, representative recordings and cumulative plots show the lack of effect of 50 μm AP5 on the frequency and amplitude of sEPSCs of a lamina II neuron from a spinal cord slice pretreated with 10 μm chelerythrine in one morphine-treated rat. B, original traces show the effect of 50 μm AP5 on the amplitude of monosynaptic EPSCs of the lamina II neuron from a spinal cord slice pretreated with chelerythrine in a morphine-treated rat. C and D, summary data of the effect of 50 μm AP5 on the mean frequency and amplitude of sEPSCs (n = 10 neurons) and the amplitude of evoked EPSCs (n = 12 neurons) in spinal cord slices pretreated with chelerythrine in morphine-treated rats. Note that the base-line frequency of sEPSCs by chelerythrine treatment in morphine-treated rats was normalized to that of vehicle-treated rats.