Figure 3.
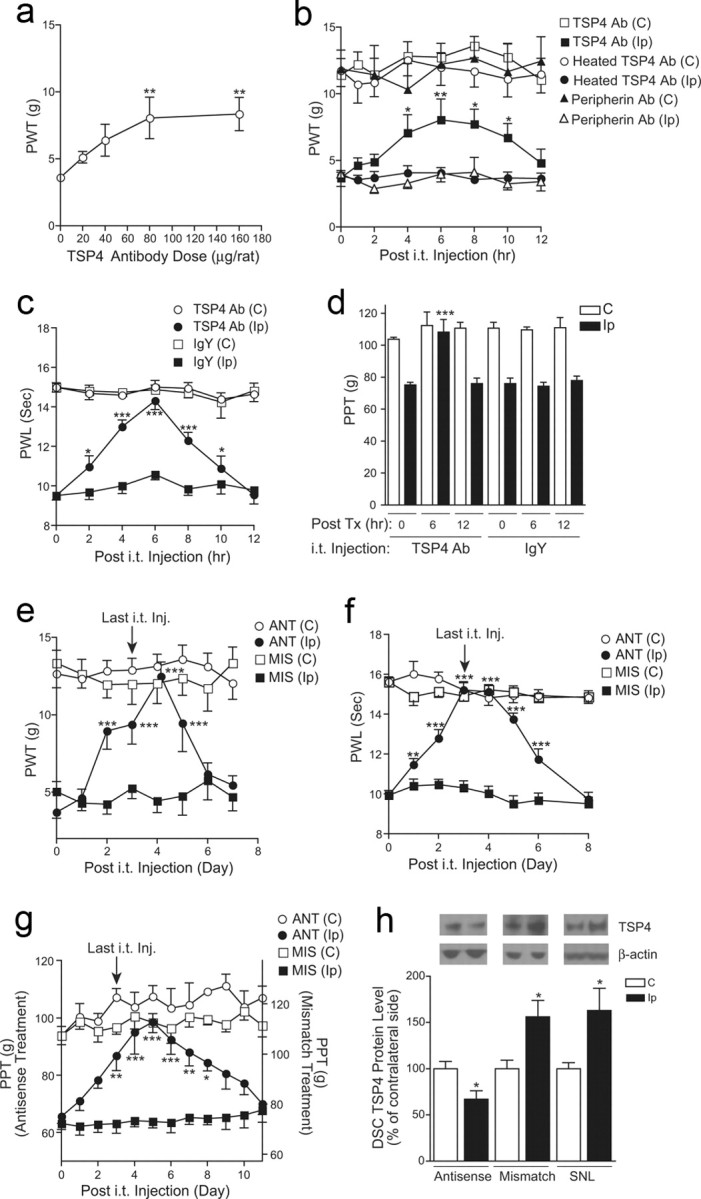
Blocking injury-induced spinal TSP4 resulted in reversal of behavioral hypersensitivities. a, Bolus intrathecal injection of TSP4 antibodies dose dependently reversed injury-induced tactile allodynia in SNL rats. Behavioral test on the injury side started 6 h after the bolus injection of TSP4 antibodies. Data shown are the mean ± SEM of 3–6 rats in each group. **p < 0.01 compared with the pretreatment level, as determined by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison tests. b, Bolus intrathecal injection of TSP4 antibodies (80 μg/rat) reversed injury-induced tactile allodynia in SNL rats without affecting the behavioral thresholds on the noninjury side. The anti-allodynic effect of TSP4 antibodies had an onset time of 4 h, peaked at 6 h, and had a duration of >6 h. Neither heated TSP4 antibodies nor antibodies against another protein, peripherin, showed anti-allodynia effects. Data shown are the mean ± SEM of 6 rats in each group. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 compared with the pretreatment level as determined by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. c, d, Bolus intrathecal injection of TSP4 antibodies (80 μg/rat) reversed injury-induced thermal hyperalgesia (c) and mechanical hyperalgesia (d) in SNL rats without affecting the behavioral thresholds on the noninjury side. The same dose of chicken IgY was used as control. To avoid sensitization of the hindpaw in paw pressure testing, mechanical hyperalgesia was tested in a 6 h interval as shown (d). Data shown are the mean ± SEM of 5–6 rats in each group. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 compared with the pretreatment level, as determined by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. e–g, Daily intrathecal injection of TSP4 antisense (ANT), but not mismatch (MIS), oligodeoxynucleotides (50 μg/rat/d) for 4 d reversed injury-induced tactile allodynia (e), thermal hyperalgesia (f), and mechanical hyperalgesia (g) in SNL rats. Behavioral tests were performed before each daily injection and daily after the last injection. Depending on the modality tested, the anti-nociceptive effect of TSP4 antisense oligodeoxynucleotides had an onset time of 1–3 d, peaked at 3–5 d, and lasted for >2–5 d after the last injection. The baseline PPT value for the mismatch treatment (g, right y-axis) was higher than that in the antisense treatment due to the conditioning adaptive increase in PPT (as shown in Fig. 1c) in the same group of rats that was used for the antisense treatment first, followed by the mismatch treatment at least 48 h apart. Data shown are the mean ± SEM of ≥5 rats in each group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 compared with the pretreatment level as determined by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. h, Intrathecal TSP4 antisense treatment (50 μg/rat/d for 4 d) blocked injury-induced TSP4 expression in dorsal spinal cord. L5/6 dorsal spinal cord (DSC) samples were collected 1 d after the last oligodeoxynucleotide treatment from SNL rats and were subjected to Western blot analyses. Representative Western blot bands are shown on top of each bar group. Data shown are the mean ± SEM of ≥7 rats in each group. SNL, 6-week SNL rats without treatment; C, Contralateral; Ip, ipsilateral.
