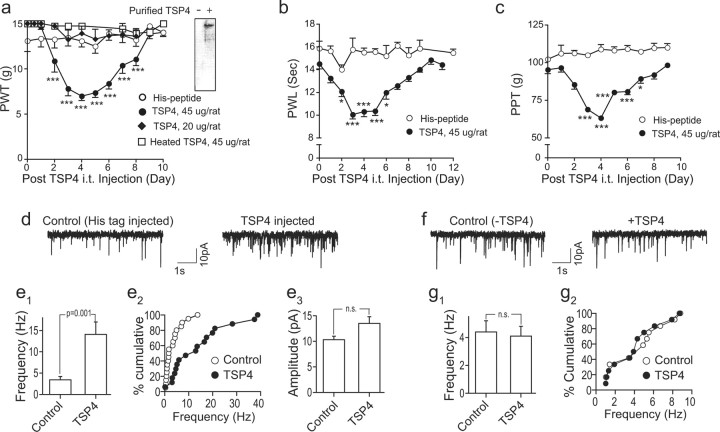
Figure 9.
Increased spinal TSP4 is sufficient to induce dorsal horn neuron sensitization and behavioral hypersensitivities through a chronic mechanism. a–c, Bolus intrathecal injection of 45 μg/rat TSP4 into L5/6 spinal regions of naive rats at time 0 led to long-lasting and reversible hindpaw hypersensitivities (averaged from both sides) assessed by blind daily behavioral test, including tactile allodynia (a), thermal hyperalgesia (b), and mechanical hyperalgesia (c). Intrathecal injection of 20 μg/rat TSP4 proteins, heated (45 μg/rat) TSP4 proteins (a), equal molar dose of His-tag peptides (a–c) did not cause behavioral hypersensitivities or alter baseline behavioral thresholds. Western blot showing purified TSP4-His fusion proteins detected by TSP4 antibodies (a, inset). Data presented are mean ± SEM of 5–6 rats in each group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 compared with pretreatment level by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. d, e, Intrathecal injection of TSP4 proteins into L5/6 spinal regions induced spinal neuron sensitization in naive rats that correlated with behavioral hypersensitivities. (d) Representative currents of AMPA receptor-mediated mEPSCs from superficial dorsal horn neuron whole-cell patch recording in L5 spinal cord slices of rats injected intrathecally with equal molar doses of His-tag peptides (Control) or TSP4-His fusion proteins (TSP4; 45 μg/rat) 4 d earlier. Intrathecal TSP4 proteins induced an increase in the average frequency (e1) as well as cumulative frequency distribution (e2), but not amplitude (e3), of mEPSCs. Data presented are summarized mean ± SEM of a total of 17–20 dorsal horn neurons recorded from spinal cord slices of 5 rats in each group. f, g, Acute application of TSP4 proteins to spinal cord slices did not alter mEPSCs in dorsal horn neurons. mEPSCs from naive rat L5 superficial dorsal horn neurons were recorded under identical conditions for spinal cord slice recording (d, e1–e3) except that TSP4 proteins were added to the recording bath for 15 min. Representative traces of mEPSC before and after bath application of 15 μg/mL TSP4 (f), a concentration that is similar to the spinal TSP4 concentration in vivo at the first injection day that caused behavioral and dorsal horn neuron sensitization later as shown in a–e, assuming the rate of CSF formation is 2.2 μl/min, approximately 3 mL/d/rat (Cserr, 1965) without considering the turnover of CSF and TSP4 proteins. Summarized graphs showing the lack of acute TSP4 effects on mEPSC average frequency (g1) and cumulative frequency distribution (g2) from rat superficial dorsal horn neurons. Data presented are the mean ± SEM of a total of 12 dorsal horn neurons recorded from spinal cord slices of 3 rats in each group. n.s., Not significant.