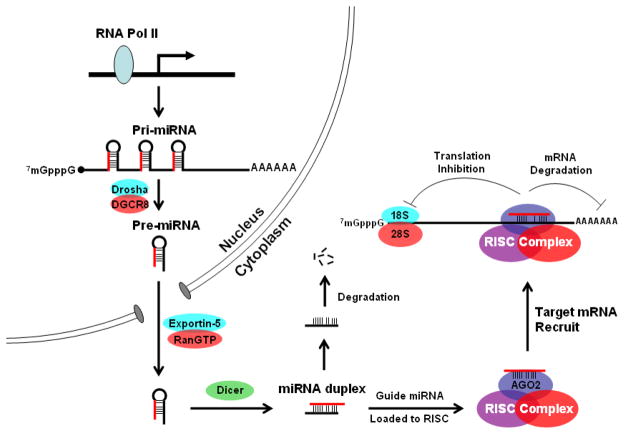
Figure 1.
Schematic view of miRNA biogenesis and functioning pathways. Genes encoding miRNA are transcribed into pri-miRNA by RNA polymerase II (RNA Pol II), the pri-miRNA is first processed by the type III RNA endonuclease, Drosha, into pre-miRNAs that are 60–70 nucleotides in length and have a stem-loop structure. The pre-miRNA is exported out of nucleus by exportin-5 and is further processed by another type III RNA endonuclease, Dicer, to generate a mature miRNA duplex 22-nucleotides in length. The sense strand of the miRNA duplex is then loaded into RISC, while the complementary strand, “star” form (*) of the miRNA duplex is degraded. The RISC complex regulates gene expression through inhibition of RNA translation or degradation of target mRNA by base-pairing the “seed region” of a miRNA to the 3′ UTR of target mRNA.